The liquid phase reaction 3R + Q→ 2P will be carried out isothermal Reactants R and Q and dilutent S will be fed at 60 ft³/min with the fol
The liquid phase reaction 3R + Q→ 2P will be carried out isothermal Reactants R and Q and dilutent S will be fed at 60 ft³/min with the fol
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
100%
plz help w/ part a i will repost for other parts
![### CSTR Reactor Design for Liquid Phase Reaction
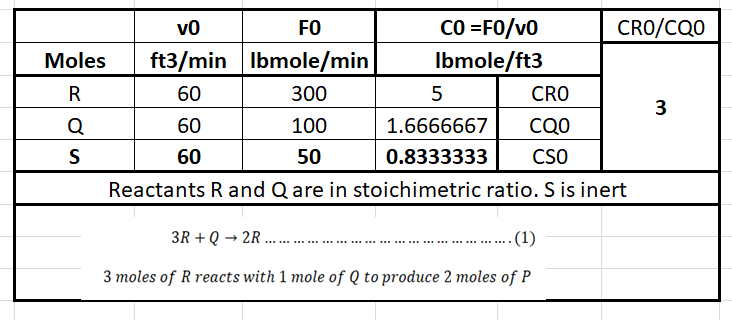
The liquid phase reaction \(3R + Q \rightarrow 2P\) will be carried out isothermally in a Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor (CSTR). The reactants R and Q, along with diluent S, will be fed at a rate of 60 ft³/min, with the following molar flow rates:
- **Species R**: 300 lbmole/min
- **Species Q**: 100 lbmole/min
- **Species S**: 50 lbmole/min
The rate law for the reaction is given by:
\[
-r_R \left( \frac{\text{lbmole}}{\text{ft}^3 \cdot \text{min}} \right) = 0.1 \times c_R^3 \times c_Q
\]
where \(c_R\) and \(c_Q\) are the concentrations of R and Q in lbmole/ft³.
### Reactor Design Specifications
The reactor is designed to achieve an 80% conversion of the limiting reactant. A consulting firm has proposed a pre-fabricated CSTR reactor with a volume of 500 cubic feet, claiming it will achieve at least 80% conversion for the given reaction.
### Tasks for Reactor Design
**A) Express the reaction rate equation in terms of conversion of the limiting reactant.**
**B) Develop the design equation for the reactor as a function of the initial concentration of the limiting reactant and its conversion.**
**C) Determine the volume of the CSTR reactor based on the given conversion and the final concentrations of all species involved in the system.**
**D) Is the design from the firm acceptable? Explain why or why not.**
These tasks will guide the evaluation of the reactor design to ensure that it meets the conversion requirements and operates efficiently.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fd47fc2c3-8f4b-4085-b234-bc909be774e3%2Fa1471dd6-4692-46e4-91d4-23d333b71fe6%2Fwxcra_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### CSTR Reactor Design for Liquid Phase Reaction
The liquid phase reaction \(3R + Q \rightarrow 2P\) will be carried out isothermally in a Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor (CSTR). The reactants R and Q, along with diluent S, will be fed at a rate of 60 ft³/min, with the following molar flow rates:
- **Species R**: 300 lbmole/min
- **Species Q**: 100 lbmole/min
- **Species S**: 50 lbmole/min
The rate law for the reaction is given by:
\[
-r_R \left( \frac{\text{lbmole}}{\text{ft}^3 \cdot \text{min}} \right) = 0.1 \times c_R^3 \times c_Q
\]
where \(c_R\) and \(c_Q\) are the concentrations of R and Q in lbmole/ft³.
### Reactor Design Specifications
The reactor is designed to achieve an 80% conversion of the limiting reactant. A consulting firm has proposed a pre-fabricated CSTR reactor with a volume of 500 cubic feet, claiming it will achieve at least 80% conversion for the given reaction.
### Tasks for Reactor Design
**A) Express the reaction rate equation in terms of conversion of the limiting reactant.**
**B) Develop the design equation for the reactor as a function of the initial concentration of the limiting reactant and its conversion.**
**C) Determine the volume of the CSTR reactor based on the given conversion and the final concentrations of all species involved in the system.**
**D) Is the design from the firm acceptable? Explain why or why not.**
These tasks will guide the evaluation of the reactor design to ensure that it meets the conversion requirements and operates efficiently.
Expert Solution
Step 1: The Limiting reactant
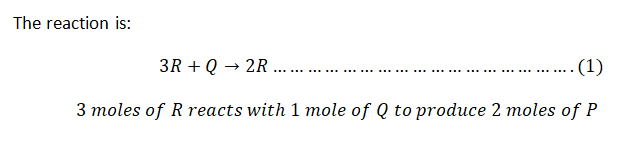
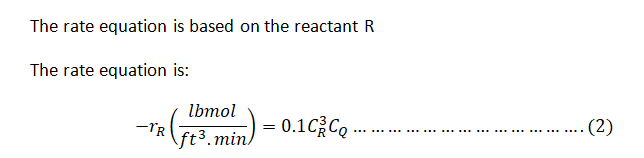
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The