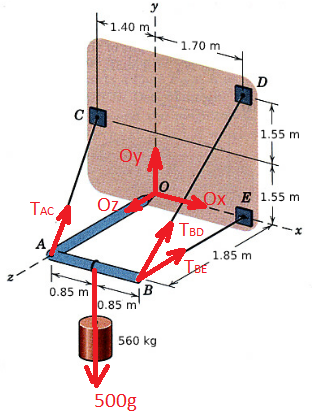
The light right-angle boom which supports the 560-kg cylinder is supported by three cables and a ball-and-socket joint at O attached to the vertical x-y surface. Determine the reactions at O and the cable tensions. A Answers: Ox i TAC i C K 0.85 m y 1.40 m! 0.85 m B 560 kg 1.70 m 1.85 m N Oy= N TBD D E 1.55 m 1.55 m Mi N O₂ = i N TBE = i N N
The light right-angle boom which supports the 560-kg cylinder is supported by three cables and a ball-and-socket joint at O attached to the vertical x-y surface. Determine the reactions at O and the cable tensions. A Answers: Ox i TAC i C K 0.85 m y 1.40 m! 0.85 m B 560 kg 1.70 m 1.85 m N Oy= N TBD D E 1.55 m 1.55 m Mi N O₂ = i N TBE = i N N
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Please don't provide handwritten solution .....

Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates a light right-angle boom system supporting a 560-kg cylinder. The boom is secured using three cables and is connected via a ball-and-socket joint at point O, which is fixed to the vertical x-y surface. The task is to determine the reactions at point O and the tensions in the cables.
### Diagram Explanation:
- **Structure**: The right-angle boom forms a triangular arrangement with support at point O. It connects with points A, B, C, D, and E.
- **Components**:
- **Cylinder**: Weighs 560 kg and hangs vertically from point A.
- **Cables**:
- Cable from C to A (denoted as \(T_{AC}\)).
- Cable from B to D (denoted as \(T_{BD}\)).
- Cable from E to B (denoted as \(T_{BE}\)).
- **Coordinates**:
- Points establish dimensions along the x, y, and z axes to define positions and distances.
- \( O \) is the origin.
- Dimensions detail:
- \(1.40 \, \text{m}\) and \(1.70 \, \text{m}\) define distances between O, C, and E on \(y\).
- \(1.55 \, \text{m}\) defines height of points D and E on \(y\).
- \(0.85 \, \text{m}\) separates A from the z-axis plane.
- \(1.85 \, \text{m}\) horizontal span from O to E on the x-axis.
- \(0.85 \, \text{m}\) distance from O to B on the z-axis.
### Required Calculations:
- **Reactions at O**:
- \(O_x\), \(O_y\), and \(O_z\) are the reactions in the x, y, and z directions, respectively.
- **Cable Tensions**:
- \(T_{AC}\), \(T_{BD}\), and \(T_{BE}\) represent the tensions in cables CA, BD, and BE, respectively.
### Answer Fields:
- Spaces provided to input values for the above calculations, measured in Newtons (N).
This exercise is relevant to studies in statics, exploring balance and forces within mechanical systems.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Draw the free-body diagram of right angle boom
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 17 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY