The length of the unit vector AB has a magnitude of _____ m.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
The length of the unit
![choice would be the vector AC.
sion r x F for the moment of a 1
to take moments directly about any
any point on the line of action of the
the A-components indicate that they
3 The negative signs associated with
shown on the free-body diagram.
tion in this problem is the freedom
is a vector from the moment center to
permits the choice of an axis that
axis. In this problem this freedom
2 Recall that the vectorr in the expres-
2.5 m 3 m
4.5 m
152 Chapter 3 Equilibrium
The welded tubular frame is segured to the horizontal x-y plane by a ban-
and-socket joint at A and receives support from the loose-fitting ring at B. Under
the action of the 2-kN load, rotation about a line from A to B is prevented by the
cable CD, and the frame is stable in the position shown. Neglect the weight of
the frame compared with the applied load and determine the tension T in the
cable, the reaction at the ring, and the reaction components at A.
SAMPLE PROBLEM 3/7
2 kN
6 m
2.5 m
А
Solufion. The system is clearly three-dimensional with no lines or planes of
symmetry, and therefore the problem must be analyzed as a general space sys-
tem of forces. The free-body diagram is drawm, where the ring reaction is shown
in terms of its two components. All unknowns except T may be eliminated by a
moment sum about the line AB. The direction of AB is specified by the unit
(4.5j + 6k) = (3j + 4k). The moment of T about AB
1 m
y
E
Bx
1
1 vector n =
Te
F= 2 kN
is the component in the direction of AB of the vector moment about the point A
and equals r1 × T.n. Similarly the moment of the applied load F about AB is
r2 x F.n. With CD = /46.2 m, the vector expressions for T, F, r1, and r2 are
V62 + 4.52
bet/
B2
r2
n
T.
(2i + 2.5j – 6k)
46.2
F = 2j kN
%3D
T =
Ay.
%3D
D\
2)
ri = -i + 2.5j m
r, = 2.5i + 6k m
Az
The moment equation now becomes
В
T
[EMAB = 0] (-i+ 2.5j) x
(2i + 2.5j – 6k) (3j + 4k)
46.2
АВ
T1 T.n
+ (2.5i + 6k) × (2j) (3j + 4k) = 0
%3D
rị xT
Completion of the vector operations gives
48T
+ 20 = 0
T = 2.83 kN
Ans.
-y
|
46.2
and the components of T become
Helpful Hints
T = 0.833 kN
T, = 1.042 kN
T, = -2.50 kN
1 The advantage of using vector nota-
We may find the remaining unknowns by moment and force summations as
follows:
permits the choice of an axis that
eliminates five of the unknowns.
[EM, = 0]
2(2.5) – 4.5B, - 1.042(3) = 0
%3D
B, = 0.417 kN
%3D
[EM, = 0]
4.5B, - 2(6) – 1.042(6) = 0
Ans.
B, = 4.06 kN
%3D
[EF, = 0]
A, + 0.417 + 0.833 = 0
Ans.
force
A, = -1.250 kN
3 EF, = 0]
A, + 2 + 1.042 = 0
Ans.
A, = -3.04 kN
equally simple
choice would be the vector AC.
[EF, = 0]
force. Instead of r1, an
%3D
A, + 4.06 – 2.50 = 0
Ans.
A, = -1.556 kN
Ans.
those
are in the opposite direction to
shown on the free-body diagra](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F6cf78908-a1f9-4330-9ece-f4021df10613%2Fbdacdc4a-cb5b-4b14-8a56-8951ecae36f9%2Ftz1pvtm_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:choice would be the vector AC.
sion r x F for the moment of a 1
to take moments directly about any
any point on the line of action of the
the A-components indicate that they
3 The negative signs associated with
shown on the free-body diagram.
tion in this problem is the freedom
is a vector from the moment center to
permits the choice of an axis that
axis. In this problem this freedom
2 Recall that the vectorr in the expres-
2.5 m 3 m
4.5 m
152 Chapter 3 Equilibrium
The welded tubular frame is segured to the horizontal x-y plane by a ban-
and-socket joint at A and receives support from the loose-fitting ring at B. Under
the action of the 2-kN load, rotation about a line from A to B is prevented by the
cable CD, and the frame is stable in the position shown. Neglect the weight of
the frame compared with the applied load and determine the tension T in the
cable, the reaction at the ring, and the reaction components at A.
SAMPLE PROBLEM 3/7
2 kN
6 m
2.5 m
А
Solufion. The system is clearly three-dimensional with no lines or planes of
symmetry, and therefore the problem must be analyzed as a general space sys-
tem of forces. The free-body diagram is drawm, where the ring reaction is shown
in terms of its two components. All unknowns except T may be eliminated by a
moment sum about the line AB. The direction of AB is specified by the unit
(4.5j + 6k) = (3j + 4k). The moment of T about AB
1 m
y
E
Bx
1
1 vector n =
Te
F= 2 kN
is the component in the direction of AB of the vector moment about the point A
and equals r1 × T.n. Similarly the moment of the applied load F about AB is
r2 x F.n. With CD = /46.2 m, the vector expressions for T, F, r1, and r2 are
V62 + 4.52
bet/
B2
r2
n
T.
(2i + 2.5j – 6k)
46.2
F = 2j kN
%3D
T =
Ay.
%3D
D\
2)
ri = -i + 2.5j m
r, = 2.5i + 6k m
Az
The moment equation now becomes
В
T
[EMAB = 0] (-i+ 2.5j) x
(2i + 2.5j – 6k) (3j + 4k)
46.2
АВ
T1 T.n
+ (2.5i + 6k) × (2j) (3j + 4k) = 0
%3D
rị xT
Completion of the vector operations gives
48T
+ 20 = 0
T = 2.83 kN
Ans.
-y
|
46.2
and the components of T become
Helpful Hints
T = 0.833 kN
T, = 1.042 kN
T, = -2.50 kN
1 The advantage of using vector nota-
We may find the remaining unknowns by moment and force summations as
follows:
permits the choice of an axis that
eliminates five of the unknowns.
[EM, = 0]
2(2.5) – 4.5B, - 1.042(3) = 0
%3D
B, = 0.417 kN
%3D
[EM, = 0]
4.5B, - 2(6) – 1.042(6) = 0
Ans.
B, = 4.06 kN
%3D
[EF, = 0]
A, + 0.417 + 0.833 = 0
Ans.
force
A, = -1.250 kN
3 EF, = 0]
A, + 2 + 1.042 = 0
Ans.
A, = -3.04 kN
equally simple
choice would be the vector AC.
[EF, = 0]
force. Instead of r1, an
%3D
A, + 4.06 – 2.50 = 0
Ans.
A, = -1.556 kN
Ans.
those
are in the opposite direction to
shown on the free-body diagra
Expert Solution
Step 1
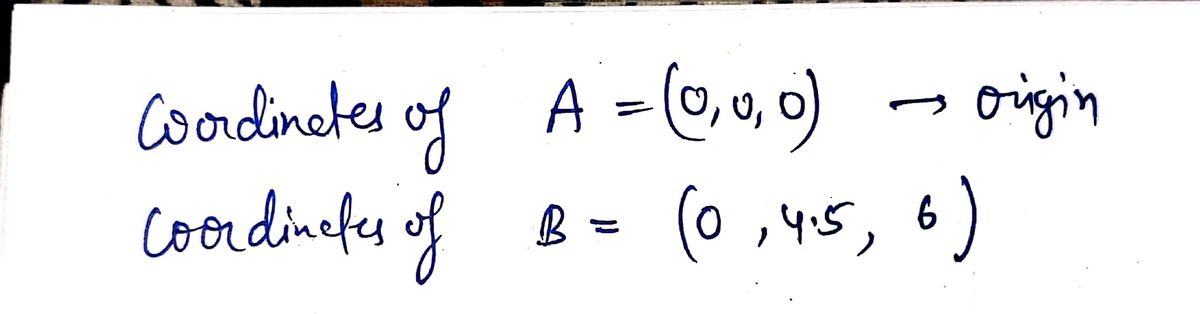
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY