The genes below have been knocked out (loss of function). Draw what the cell would look like during the appropriately affected stage of mitosis. State what stage you are depicting on your drawing. (Each gene knockout is occurring in a different cell; you should have a drawing of the affected cell for each). 1. Separase, 2. Cohesin
The genes below have been knocked out (loss of function). Draw what the cell would look like during the appropriately affected stage of mitosis. State what stage you are depicting on your drawing. (Each gene knockout is occurring in a different cell; you should have a drawing of the affected cell for each).
1. Separase,
2. Cohesin
A gene is a stretch of nucleotides present in the DNA. It codes for the synthesis of an RNA or protein molecule required for different functioning. When a gene is knocked out from the genome of an organism, the corresponding function of the gene is also lost.
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of two daughter cells from one parental cell. Mitosis is preceded by DNA replication in which the genetic material of a cell is duplicated to be transferred to the two daughter cells.
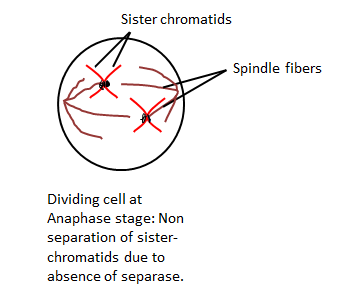
- Separase is an important protein required during the division of a cell. It is a cysteine-protease that is also known as separin. It is responsible for triggering anaphase stage of mitosis by cleaving the cohesion protein that binds the sister chromatids together. In the absence of separase, the mitotic cycle will progress but non-disjunction will occur. Most of the embryo dies at early stage due to such mutation.
The diagram depicting the affected stage is shown below:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









