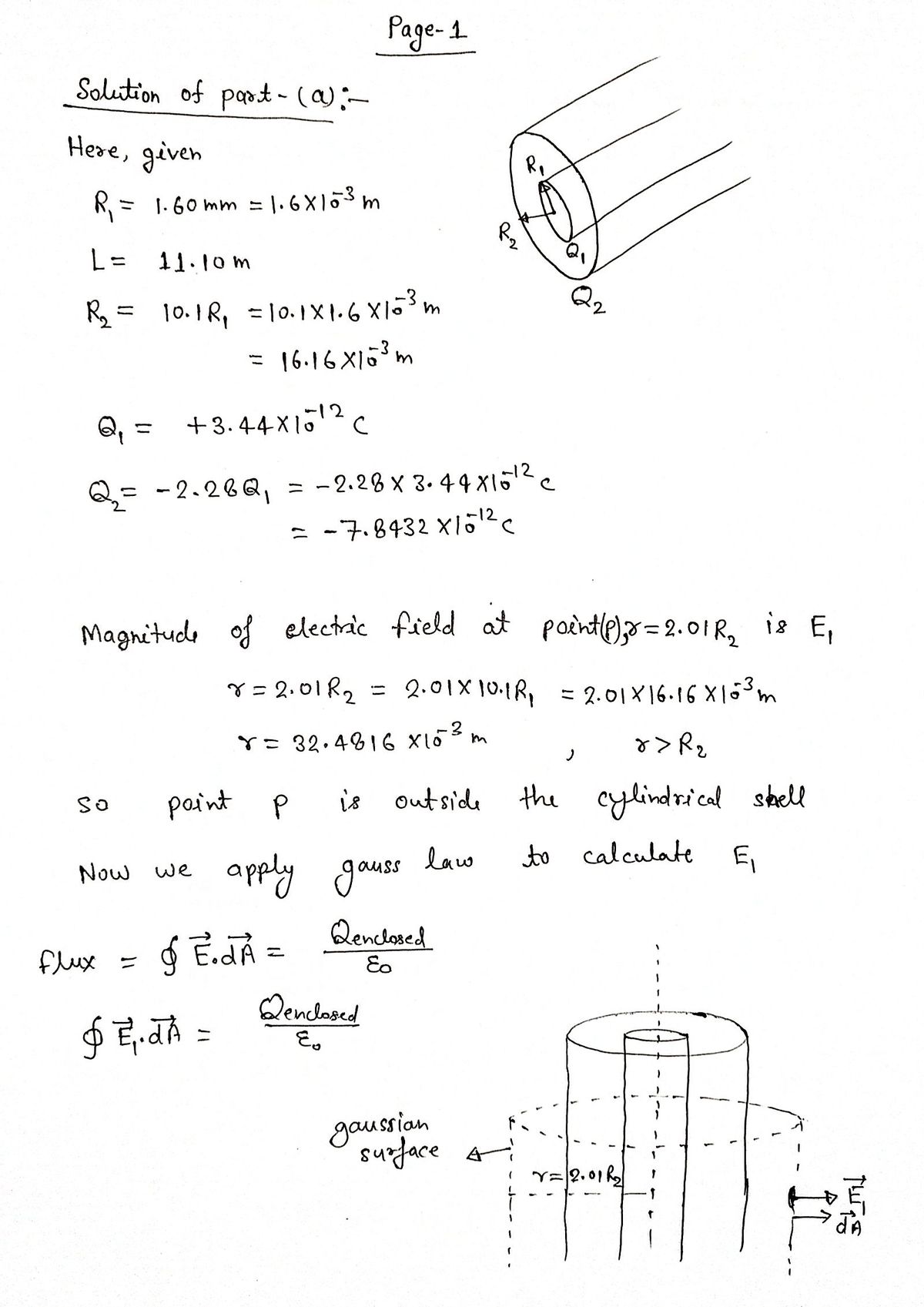
The figure is a section of a conducting rod of radius R₁ = 1.60 mm and length L = 11.10 m inside a thin-walled coaxial conducting cylindrical shell of radius R₂ = 10.1R₁ and the (same) length L. The net charge on the rod is Q₁ =+3.44 x 10-12 C; that on the shell is Q2 = -2.28Q₁. What are the (a) magnitude E and (b) direction (radially inward or outward) of the electric field at radial distance r = 2.01R₂? What are (c) E and (d) the direction at r = 5.16R₁? What is the charge on the (e) interior and (f) exterior surface of the shell? (a) Number i (b) (c) Number i (d) (e) Number i V Units Units Units 4
The figure is a section of a conducting rod of radius R₁ = 1.60 mm and length L = 11.10 m inside a thin-walled coaxial conducting cylindrical shell of radius R₂ = 10.1R₁ and the (same) length L. The net charge on the rod is Q₁ =+3.44 x 10-12 C; that on the shell is Q2 = -2.28Q₁. What are the (a) magnitude E and (b) direction (radially inward or outward) of the electric field at radial distance r = 2.01R₂? What are (c) E and (d) the direction at r = 5.16R₁? What is the charge on the (e) interior and (f) exterior surface of the shell? (a) Number i (b) (c) Number i (d) (e) Number i V Units Units Units 4
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The figure is a section of a conducting rod of radius R₁ = 1.60 mm and length L = 11.10 m inside a thin-walled coaxial conducting
cylindrical shell of radius R₂ = 10.1R₁ and the (same) length L. The net charge on the rod is Q₁ =+3.44 x 10-12 C; that on the shell is Q₂ =
-2.28Q1. What are the (a) magnitude E and (b) direction (radially inward or outward) of the electric field at radial distance r = 2.01R₂?
What are (c) E and (d) the direction at r = 5.16R₁? What is the charge on the (e) interior and (f) exterior surface of the shell?
(a) Number i
(b)
IF
(d)
(c) Number i
(e) Number
IN
R₂
Units
Units
Units
Ri
e
Q2
>
4
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images
