The accompanying data represent the number of days absent, x, and the final exam score, y, for a sample of college students in a general education course at a large state university. Absences and Final Exam Scores No. of absences, x 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Final exam score, y 89.7 86.1 83.6 81.8 78.7 74.1 64.4 71.2 64.5 66.4 Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient n 3 0.997 4 0.950 5 0.878 6 0.811 7 0.754 8 0.707 9 0.666 10 0.632 11 0.602 12 0.576 13 0.553 14 0.532 15 0.514 16 0.497 17 0.482 18 0.468 19 0.456 20 0.444 21 0.433 22 0.423 23 0.413 24 0.404 25 0.396 26 0.388 27 0.381 28 0.374 29 0.367 30 0.361 n (a) The least-squaresregressionline treating number of absences as the explanatory variable and the final exam score as the response variable. y=negative 2.907−2.907x+89.133 (b) Interpret the slope and the y-intercept, if appropriate. Choose the correct answer below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. Round to 3 decimal places as needed. A. For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops _______ points, on average. The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is ________. B. For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops _______ points, on average. It is not appropriate to interpret the y-intercept. C. The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is _________. It is not appropriate to interpret the slope. D. It is not appropriate to interpret the slope or the y-intercept.
The accompanying data represent the number of days absent, x, and the final exam score, y, for a sample of college students in a general education course at a large state university. Absences and Final Exam Scores No. of absences, x 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Final exam score, y 89.7 86.1 83.6 81.8 78.7 74.1 64.4 71.2 64.5 66.4 Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient n 3 0.997 4 0.950 5 0.878 6 0.811 7 0.754 8 0.707 9 0.666 10 0.632 11 0.602 12 0.576 13 0.553 14 0.532 15 0.514 16 0.497 17 0.482 18 0.468 19 0.456 20 0.444 21 0.433 22 0.423 23 0.413 24 0.404 25 0.396 26 0.388 27 0.381 28 0.374 29 0.367 30 0.361 n (a) The least-squaresregressionline treating number of absences as the explanatory variable and the final exam score as the response variable. y=negative 2.907−2.907x+89.133 (b) Interpret the slope and the y-intercept, if appropriate. Choose the correct answer below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice. Round to 3 decimal places as needed. A. For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops _______ points, on average. The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is ________. B. For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops _______ points, on average. It is not appropriate to interpret the y-intercept. C. The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is _________. It is not appropriate to interpret the slope. D. It is not appropriate to interpret the slope or the y-intercept.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
The accompanying data represent the number of days absent, x, and the final exam score, y, for a sample of college students in a general education course at a large state university.
Absences and Final Exam Scores
|
No. of
absences, x
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Final
exam score, y
|
89.7
|
86.1
|
83.6
|
81.8
|
78.7
|
74.1
|
64.4
|
71.2
|
64.5
|
66.4
|
Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient
n
3 0.997
4 0.950
5 0.878
6 0.811
7 0.754
8 0.707
9 0.666
10 0.632
11 0.602
12 0.576
13 0.553
14 0.532
15 0.514
16 0.497
17 0.482
18 0.468
19 0.456
20 0.444
21 0.433
22 0.423
23 0.413
24 0.404
25 0.396
26 0.388
27 0.381
28 0.374
29 0.367
30 0.361
n
n
3 0.997
4 0.950
5 0.878
6 0.811
7 0.754
8 0.707
9 0.666
10 0.632
11 0.602
12 0.576
13 0.553
14 0.532
15 0.514
16 0.497
17 0.482
18 0.468
19 0.456
20 0.444
21 0.433
22 0.423
23 0.413
24 0.404
25 0.396
26 0.388
27 0.381
28 0.374
29 0.367
30 0.361
n
(a) The least-squaresregressionline treating number of absences as the explanatory variable and the final exam score as the response variable.
y=negative 2.907−2.907x+89.133
(b) Interpret the slope and the y-intercept, if appropriate. Choose the correct answer below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
Round to 3 decimal places as needed.
For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops
_______ points, on average. The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is ________.
For every additional absence, a student's final exam score drops _______ points, on average. It is not appropriate to interpret the y-intercept.
The average final exam score of students who miss no classes is
_________. It is not appropriate to interpret the slope.
It is not appropriate to interpret the slope or the y-intercept.
Expert Solution
(a)
Procedure to conduct regression analysis using Excel:
- Enter the data of x and y in an excel sheet.
- Go to Data > Data Analysis.
- From Analysis Tool, choose Regression and click OK.
- In Input Y Range, select the data of Final exam score, y.
- In Input X Range, select the data of No. of absences, x.
- Click OK.
Output:
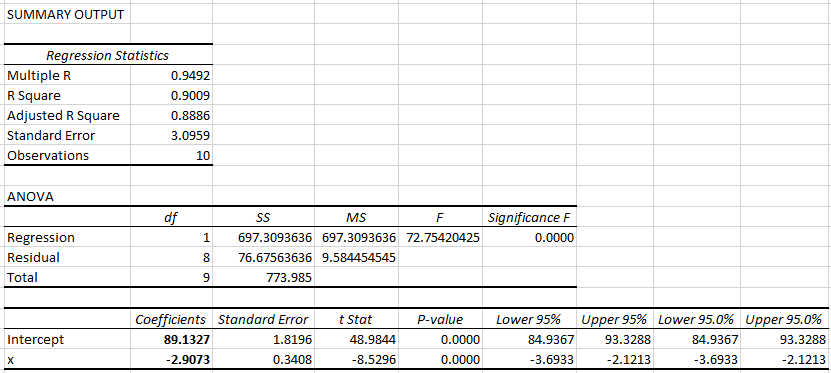
From the output, the least-squares regression line treating number of absences as the explanatory variable and the final exam score as the response variable is .
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman