Nitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 50 L tank with 6.5 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 4.8 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 3.3 mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. mol X Ś ?
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 50 L tank with 6.5 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 4.8 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 3.3 mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. mol X Ś ?
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter17: Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 38A
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Nitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to
form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 50 L tank with 6.5 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that
it contains 4.8 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas.
The engineer then adds another 3.3 mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide
after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
00.
Ar
mol
x10
Ś
?
Explanation
© 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
Check
0:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
this one is asking for mol

Transcribed Image Text:While ethanol (CH3CH₂OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by reacting ethylene
(CH₂CH₂) with water vapor at elevated temperatures.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 75 L tank with 32. mol of ethylene gas and 28. mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium
he determines that it contains 25.4 mol of ethylene gas and 21.4 mol of water vapor.
The engineer then adds another 9.3 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of ethanol after equilibrium is
reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
olo
Ar
mol
x10
X
Ś ?
Explanation
© 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
Check
Solution
Follow-up Question
this one is asking for atm
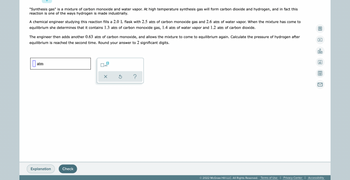
Transcribed Image Text:"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this
reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 2.0 L flask with 2.5 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 2.6 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to
equilibrium she determines that it contains 1.3 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 1.4 atm of water vapor and 1.2 atm of carbon dioxide.
The engineer then adds another 0.63 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of hydrogen after
equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
0 atm
x10
X
3
?
Explanation
© 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
Check
0:
A
olo
Ar
1
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning