Statistics Question

Introduction:
Define X as the random variable of interest here.
It is given that X has a normal distribution with population mean μ = 50, and population standard deviation σ = 10.
6.106.
The sampling distribution of the sample mean, X̄, based on a sample of size n, taken from a population with expectation μ and standard deviation σ, has expectation μX̄ = μ and standard deviation σX̄ = σ/√n.
If the sample size is large (n ≥ 30), or the population distribution is normal, then by the central limit theorem, the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normal, with parameters μX̄ and σX̄.
The sample size is, n = 13.
Here, as X is already normally distributed, X̄ has a normal distribution irrespective of the sample size.
The mean of the sampling distribution the sample mean is:
μX̄
= μ
= 50.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution the sample mean is:
σX̄
= σ/√n
= 10/√13
≈ 2.7735.
The probability that the sample mean will be within 1 unit of the population mean is calculated below:
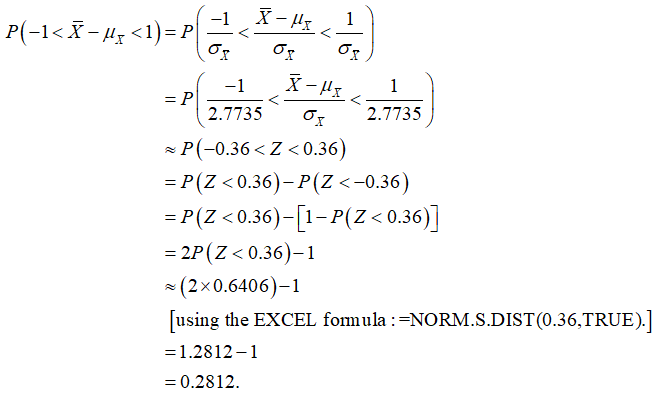
Thus, the probability that the sample mean will be within 1 unit of the population mean is is 0.2812.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









