Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of μ = 75.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of σ = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute. The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute. The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b) even though the sample size does not exceed 30? - A. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. - B. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of individual items is a normal distribution for any sample size. - C. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size. - D. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size. Click to select your answer(s).
Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of μ = 75.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of σ = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute. The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute. The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b) even though the sample size does not exceed 30? - A. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. - B. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of individual items is a normal distribution for any sample size. - C. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size. - D. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size. Click to select your answer(s).
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of μ = 75.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of σ = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute.
The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 71 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute.
The probability is ________ (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b) even though the sample size does not exceed 30?
- A. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size.
- B. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of individual items is a normal distribution for any sample size.
- C. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size.
- D. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is normal regardless of sample size.
Click to select your answer(s).
Expert Solution
Step 1
Let "X" be female pulse rates in bpm.
Draw the normal curve and shade the area between z=-0.32 and z=0.32.
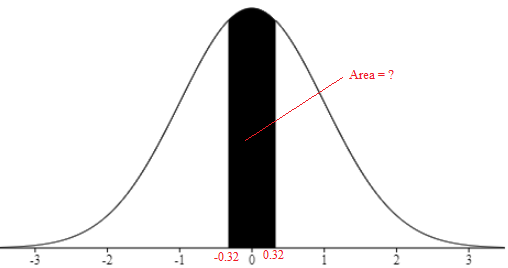
The required shaded area under the normal curve is
Refer to Standard normal table/Z-table to find the probability of z=0.32 and z=-0.32 to the left of the normal curve.
OR
Use excel formula "=NORM.S.DIST(0.32, TRUE)" and "=NORM.S.DIST(-0.32, TRUE)" to find the probability.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 25 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman