Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The image is a table displaying chemical structures labeled A to H. Here is a detailed transcription of the chemical structures:
- **A**: A linear chain of four carbon atoms with a cyano group (CN) at the end.
- **B**: A benzene ring with an amino group (NH₂) attached.
- **C**: A linear chain of four carbon atoms with a terminal alkyne (triple bond) group.
- **D**: A linear chain of five carbon atoms with a ketone group (C=O) at the second position.
- **E**: A linear chain of four carbon atoms with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to the second carbon.
- **F**: A benzene ring with a methyl group (CH₃) attached.
- **G**: A structure featuring a carboxylic acid group (COOH) adjacent to a secondary alcohol group (OH) on the second carbon of a three-carbon chain.
- **H**: A linear chain of four carbon atoms with a ketone group (C=O) on the second carbon.
This table provides various organic chemical structures commonly encountered in chemistry.

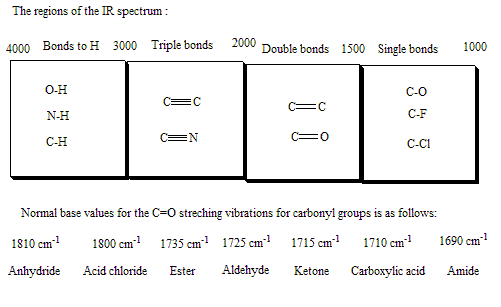
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays an infrared (IR) spectrum graph, which is commonly used in chemistry to identify functional groups within a compound.
**Graph Description:**
- **X-axis (Horizontal):** Represents wavenumber in reciprocal centimeters (cm⁻¹), ranging from 4000 to 400 cm⁻¹. Wavenumbers are inversely proportional to wavelength and directly proportional to frequency.
- **Y-axis (Vertical):** Typically represents transmittance or absorbance. Although not labeled, the downward peaks indicate regions where the compound absorbs infrared light.
- **Spectral Features:**
- The broad peak around 3300 cm⁻¹ may indicate the presence of an O-H (hydroxyl) group, which is characteristic of alcohols and phenols.
- Sharp peaks around 1700 cm⁻¹ suggest the presence of a carbonyl (C=O) group, often seen in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters.
- The region between 1000 and 1300 cm⁻¹ might indicate C-O stretching vibrations.
- Multiple peaks in the fingerprint region (≤1500 cm⁻¹) are complex but can help in identifying unique patterns correlated with specific compounds.
**Purpose of IR Spectroscopy:**
IR spectroscopy is a critical tool for identifying chemical bonds and functional groups within a molecular structure by analyzing how different molecular bonds absorb infrared light.
This spectrum would be used in educational materials to demonstrate the typical infrared absorption bands and assist students in interpreting real sample spectra.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY