random sample of 18 monthly rents for apartments on the east side has a mean of $644, with a standard deviation of $21. If we assume that the monthly rents for apartments on the east side are town is less than $ normally distributed, is there enough evidence to conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that u is less than $650? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. 圖 Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H. H, :0 合 H : 믐 (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. OSO (Choose one) ▼ (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (d) Find the p-jue. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (e) Using the 0.05 level of significance, can we conclude that the mean monthly rent for apartments on the east side is less than $650? OYes ONo 日
random sample of 18 monthly rents for apartments on the east side has a mean of $644, with a standard deviation of $21. If we assume that the monthly rents for apartments on the east side are town is less than $ normally distributed, is there enough evidence to conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that u is less than $650? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. 圖 Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H. H, :0 合 H : 믐 (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. OSO (Choose one) ▼ (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (d) Find the p-jue. (Round to three or more decimal places.) (e) Using the 0.05 level of significance, can we conclude that the mean monthly rent for apartments on the east side is less than $650? OYes ONo 日
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![**Hypothesis Testing for Mean Rent**
A rental agent claims that the mean monthly rent, μ, for apartments on the east side of town is less than $650. A random sample of 18 monthly rents for apartments on the east side has a mean of $644, with a standard deviation of $21. If we assume that the monthly rents for apartments on the east side are normally distributed, is there enough evidence to conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that μ is less than $650?
Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below.
Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
(a) **State the null hypothesis \(H_0\) and the alternative hypothesis \(H_1\).**
\[H_0: \ ☐\]
\[H_1: \ ☐\]
(b) **Determine the type of test statistic to use.**
\[ \text{(Choose one)} \ ☐\]
(c) **Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.)**
\[ \☐\]
(d) **Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.)**
\[ \☐\]
(e) **Using the 0.05 level of significance, can we conclude that the mean monthly rent for apartments on the east side is less than $650?**
\[ \text{Yes} \☐ \text{No} \☐\]
**Diagram Details**
The diagram is a matrix of symbols commonly used in statistics. It includes symbols for population mean (\(μ\)), sample mean (\(x̄\)), population standard deviation (\(σ\)), sample standard deviation (\(s\)), probability (\(p\)), and sample proportion (\(p̂\)) among others, organized in a grid without direct connections or labels, serving as a quick reference tool for selecting statistical symbols.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1d3f2bfb-a5cc-4b06-99e2-b36f9d38db79%2F1527ad55-1dd1-4d92-9a72-d43a18c7a4a4%2Fz4q95pe_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing for Mean Rent**
A rental agent claims that the mean monthly rent, μ, for apartments on the east side of town is less than $650. A random sample of 18 monthly rents for apartments on the east side has a mean of $644, with a standard deviation of $21. If we assume that the monthly rents for apartments on the east side are normally distributed, is there enough evidence to conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance, that μ is less than $650?
Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below.
Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
(a) **State the null hypothesis \(H_0\) and the alternative hypothesis \(H_1\).**
\[H_0: \ ☐\]
\[H_1: \ ☐\]
(b) **Determine the type of test statistic to use.**
\[ \text{(Choose one)} \ ☐\]
(c) **Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.)**
\[ \☐\]
(d) **Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.)**
\[ \☐\]
(e) **Using the 0.05 level of significance, can we conclude that the mean monthly rent for apartments on the east side is less than $650?**
\[ \text{Yes} \☐ \text{No} \☐\]
**Diagram Details**
The diagram is a matrix of symbols commonly used in statistics. It includes symbols for population mean (\(μ\)), sample mean (\(x̄\)), population standard deviation (\(σ\)), sample standard deviation (\(s\)), probability (\(p\)), and sample proportion (\(p̂\)) among others, organized in a grid without direct connections or labels, serving as a quick reference tool for selecting statistical symbols.
Expert Solution
Step 1
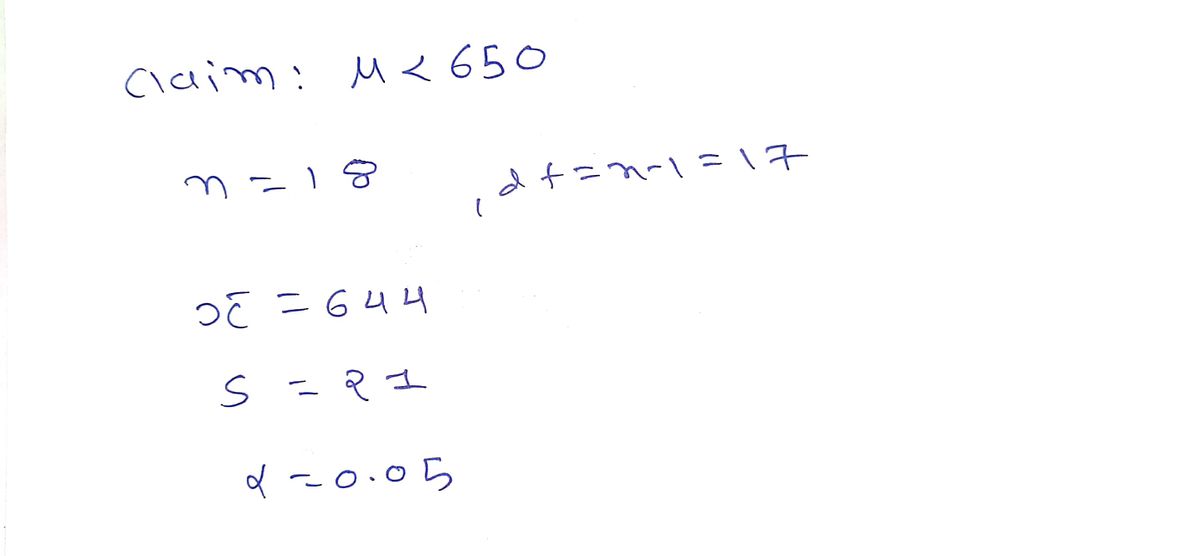
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman