Questions 1. What is transistor, how does it work and where are they used? 2. Solve the following circuit to find IB, IC, IE currents and VCE, VCB Voltages. Assume the VBE voltage is 700mV. (B = 306)
Questions 1. What is transistor, how does it work and where are they used? 2. Solve the following circuit to find IB, IC, IE currents and VCE, VCB Voltages. Assume the VBE voltage is 700mV. (B = 306)
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter30: Dc Motors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6RQ: What is CEMF?
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Questions
1. What is transistor, how does it work and where are they used?
2. Solve the following circuit to find IB, IC, IE currents and VCE, VCB Voltages. Assume
the VBE voltage is 700mV. (B = 306)
+
VCC
9V
IB
>RB
Ic
· 200ΚΩ
+
B
V BE
Rc
100Ω
2N3904
E
3. Make all simulations of the experiment 3 and add your graphs.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
pease fill the table and graphic
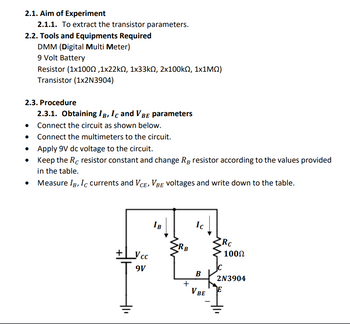
Transcribed Image Text:2.1. Aim of Experiment
2.1.1. To extract the transistor parameters.
2.2. Tools and Equipments Required
DMM (Digital Multi Meter)
9 Volt Battery
Resistor (1x100Ω,1x22kΩ, 1x33kΩ, 2x100kΩ, 1x1ΜΩ)
Transistor (1x2N3904)
2.3. Procedure
2.3.1. Obtaining IB, IC and VBE parameters
• Connect the circuit as shown below.
Connect the multimeters to the circuit.
• Apply 9V dc voltage to the circuit.
•
Keep the Rc resistor constant and change RB resistor according to the values provided
in the table.
Measure IB, IC currents and VCE, VBE voltages and write down to the table.
+Vcc
9V
IB
RB
+
Ic
B
V BE
Rc
100Ω
2N3904
E
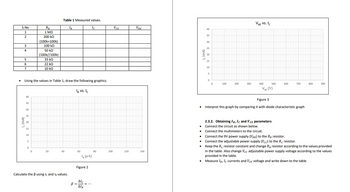
Transcribed Image Text:S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(mA)
• Using the values in Table 1, draw the following graphics.
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
RB
1 ΜΩ
200 kQ
(100k+100k)
100 kQ
50 ΚΩ
(100k//100k)
33 ΚΩ
22 ΚΩ
10 kQ
0
Table 1 Measured values.
IB
Ic
20
40
Calculate the ß using Ic and le values.
IB VS. Ic
60
(μA)
Figure 2
B = ==
Alc
ΔΙΒ
80
100
VCE
120
VBE
140
.
.
c (mA)
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
100
200
300
VBE VS. Ic
400
500
VBE (V)
600
2.3.2. Obtaining IB, IC and VCE parameters
Connect the circuit as shown below.
700
Figure 3
Interpret this graph by comparing it with diode characteristic graph
800
900
Connect the multimeters to the circuit.
Connect the 9V power supply (VBB) to the RB resistor.
Connect the adjustable power supply (Vcc) to the Rc resistor.
Keep the Rc resistor constant and change RB resistor according to the values provided
the table. Also change Vcc adjustable power supply voltage according to the values
provided in the table.
Measure IB, IC currents and VCE voltage and write down to the table.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning