Q8.4 Structure CH3 CH3 ВЕ .C -E D I II What substituent is positioned at B on Structure II? O -H O -CH3 Q8.5 Structure CH3 CH3 В ВЕ .C A -E H3C A I II What substituent is positioned at C on Structure II? O H O -CH3 Q8.6 Structure CH3 CH3 B E A H3C A F, F I II What substituent is positioned at E on Structure II? O -H -CH3
Q8.4 Structure CH3 CH3 ВЕ .C -E D I II What substituent is positioned at B on Structure II? O -H O -CH3 Q8.5 Structure CH3 CH3 В ВЕ .C A -E H3C A I II What substituent is positioned at C on Structure II? O H O -CH3 Q8.6 Structure CH3 CH3 B E A H3C A F, F I II What substituent is positioned at E on Structure II? O -H -CH3
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:### Q8.4 Structure
This question involves the transformation of a cyclohexane derivative into two different structures (I and II). The starting molecule is a cyclohexane ring with two methyl (CH₃) groups.
#### Diagrams:
- **Structure I**: Represents the cyclohexane chair conformation with substituents labeled A, B, C, D, E, and F.
- **Structure II**: Depicts the flipping of the chair conformation, altering the positions of the substituents.
**Question**: What substituent is positioned at B on Structure II?
- ○ -H
- ○ -CH₃
---
### Q8.5 Structure
This question also involves a cyclohexane derivative transforming into structures I and II. The focus is on a different substituent location compared to Q8.4.
#### Diagrams:
- **Structure I**: Displays the cyclohexane chair conformation, with substituents labeled A through F.
- **Structure II**: Shows the result of the conformational change (chair flip).
**Question**: What substituent is positioned at C on Structure II?
- ○ -H
- ○ -CH₃
---
### Q8.6 Structure
This question follows the same transformation theme but examines another substituent position on the cyclohexane ring.
#### Diagrams:
- **Structure I**: Displays the cyclohexane chair arrangement, with substituents labeled A through F.
- **Structure II**: Illustrates the conformational change due to chair flipping.
**Question**: What substituent is positioned at E on Structure II?
- ○ -H
- ○ -CH₃

Transcribed Image Text:```markdown
### Q8 Conformational Analysis of Cycloalkanes
In this question, you will look at the conformations of the following molecule:
**Molecule Diagram:**
The diagram shows a cyclohexane ring with various substituents. The substituents include methyl groups. Two conformations are depicted:
- **Conformation I and Conformation II**: Both structures feature the cyclohexane ring with different orientations of the substituents labeled A through F.
---
### Energy Costs for Interactions in Alkane Conformers:
| Interaction | Computed Energy Cost (kJ/mol)⁺ |
|---------------------------------|--------------------------------|
| H↔H eclipsed | 3.8 |
| H↔CH₃ eclipsed | 4.8 |
| CH₃↔CH₃ eclipsed | 12.6 |
| CH₃↔CH(CH₃)₂ gauche | 3.7 |
| H↔CH(CH₃)₂ gauche | (0.0) |
| H↔CH(CH₃)₂ eclipsed | 3.1 |
| CH₃↔CH(CH₃)₂ gauche | 3.6 |
| CH₃↔CH(CH₃)₂ eclipsed | 17.3 |
| H↔C(CH₃)₃ eclipsed | 2.8* |
| CH₃↔C(CH₃)₃ gauche | 13.6 |
| CH₃↔C(CH₃)₃ eclipsed | 18.7 |
| H↔e₁ eclipsed | 6.7 |
| I↔CH₃ gauche | 1.2 |
| I↔CH₃ eclipsed | 15.5 |
⁺ Values computed with Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) for structure optimization and B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,3p) for conformation energy. Calculations were performed in the gas phase (no solvent).
* Note: This result for t-butyl is peculiar since the value is less than that for isopropyl, but an explanation will be provided in office hours.
---
###
Expert Solution
Step 1
Equatorial conformation is more stable than axial confirmation.
The stable chair conformation of the given compound will be that in which maximum no. of CH3 groups will be at equatorial position. Thus the stable confirmation will be:
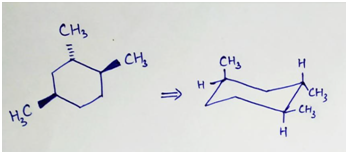
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY