Q.4. Uranium dioxide (UO,)is an oxide of uranium used in nuclear fuel rods in nuclear reactors. Calculate the mass attenuation coefficient of UO, for 1 MeV gamma rays. The density of UO, is 10 g/cm. What is their mean free path? Mean free path length (A-lambda), which is the mean distance a particle or photon travels between interactions.
Q.4. Uranium dioxide (UO,)is an oxide of uranium used in nuclear fuel rods in nuclear reactors. Calculate the mass attenuation coefficient of UO, for 1 MeV gamma rays. The density of UO, is 10 g/cm. What is their mean free path? Mean free path length (A-lambda), which is the mean distance a particle or photon travels between interactions.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Q.4. Uranium dioxide (UO,)is an oxide of uranium used in nuclear fuel
rods in nuclear reactors.
Calculate the mass attenuation coefficient of UO, for 1 MeV gamma
rays.
The density of UO, is 10 g/cm.
What is their mean free path?
Mean free path length (A-lambda), which is the mean distance a
particle or photon travels between interactions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
The mass attenuation coefficient is defined as;

Where
μ be defined as the attenuation coefficient.
ρm be defined as the mass density.
The attenuation constant for uranium is 0.0757 cm2/g and for oxygen is 0.0636 cm2/g.
Step 2
The fraction of weight U and O2 in UO2 is,
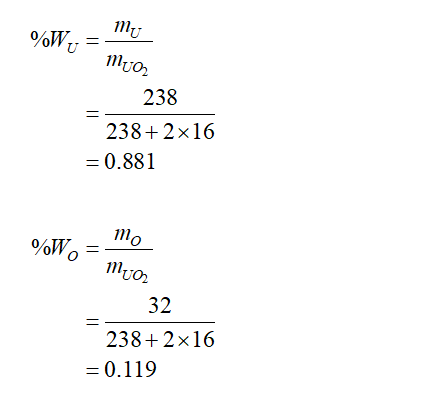
Step 3
The total mass attenuation coefficient is,
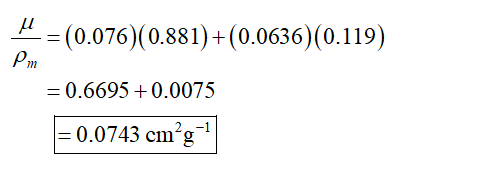
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images
