Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Provide the complete mechanism for the reaction. Please include appropriate arrows, intermediates, and formal charges.

Transcribed Image Text:### Chemical Reaction: Decarboxylation Process
**Reaction Description:**
This image illustrates a chemical reaction involving the decarboxylation of a cyclic compound. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. **Reactant:**
- The starting material is a cyclic compound featuring an alkyne group. It has a six-membered carbon ring with two ketone groups positioned at carbon 1 and carbon 5. The compound also contains an alkyne side chain bonded to the ring.
2. **Reaction Conditions:**
- **Solvent:** DME (Dimethoxyethane)
- **Condition:** Heat is applied to facilitate the reaction.
3. **Products:**
- The reaction yields a bicyclic compound characterized by a five-membered lactone ring fused to a benzene ring.
- Additionally, carbon dioxide (CO₂) is released as a by-product.
**Mechanistic Insight:**
- **Decarboxylation:** This process involves the elimination of a carboxyl group, releasing CO₂. The reaction progresses under heat, leading to the formation of a more stable product with the release of CO₂ gas.
**Graph or Diagram Details:**
- The arrows in the diagram depict the direction of the reaction from reactants to products, indicating that the reaction proceeds forward with the aid of heat. The structures of the molecules are illustrated using standard chemical notation, with lines representing chemical bonds and corners representing carbon atoms, while hydrogen atoms are typically omitted for clarity.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction is a (4+2) cycloaddition reaction between electron-rich diene and electron deficient dienophile. Diene is a compound having two double bonds and Dienophile is a compound with 1 double bond.
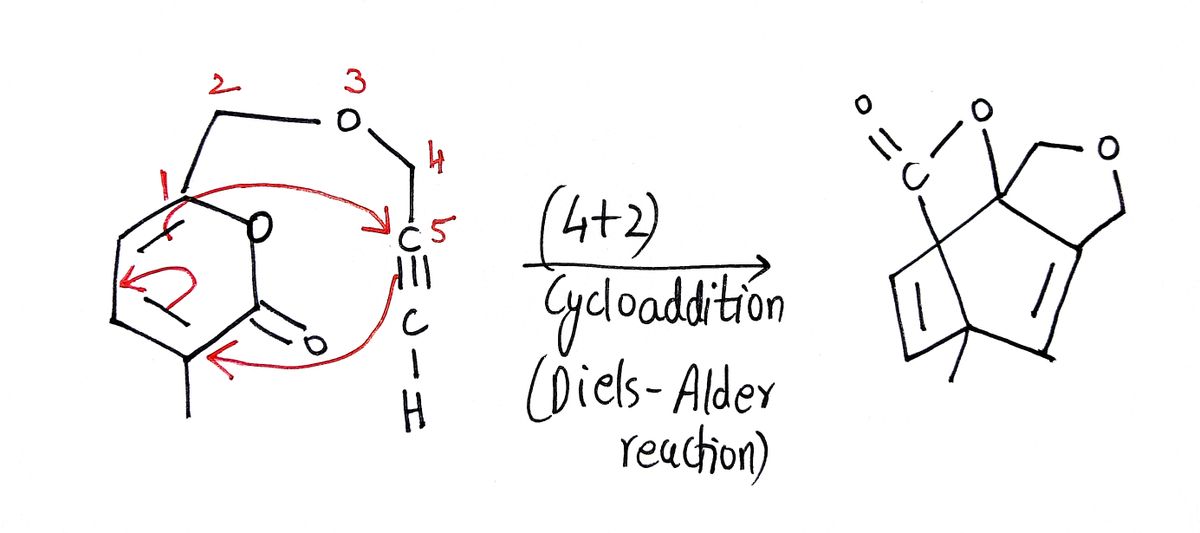
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY