Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

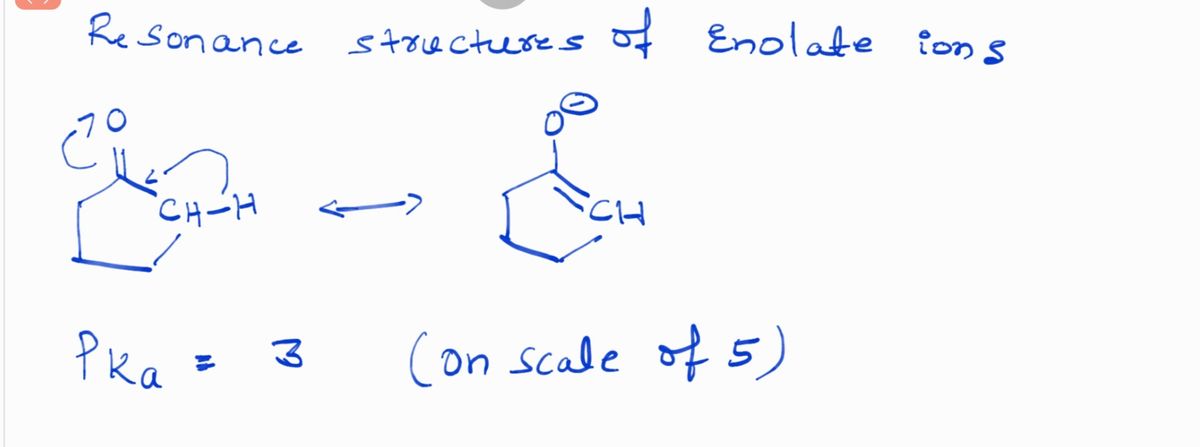
Figure A shows a cyclic ketone with the molecular formula C₅H₈O. The α-hydrogen is located on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group.
**Compound B:**

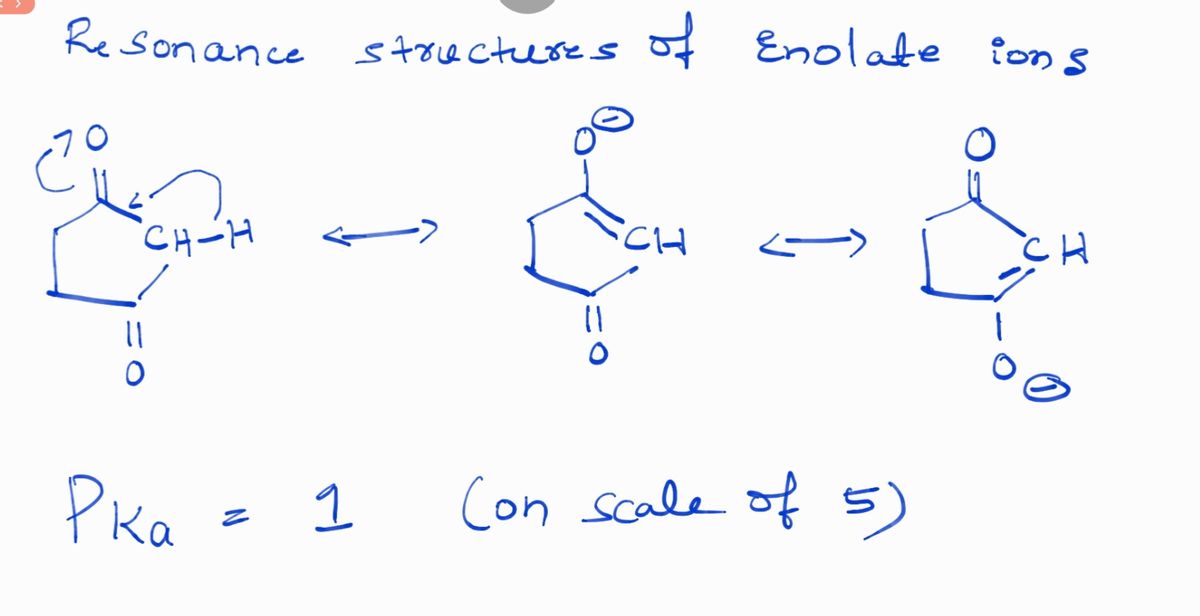
Figure B shows a cyclic dione with the molecular formula C₆H₈O₂. The α-hydrogen is located on the carbon adjacent to two carbonyl groups.
Both compounds have their structures represented with equilibrium arrows indicating the deprotonation process:
```
O
/ \
CH2 \
| /
(double arrow showing equilibrium process)
(first compound's equivalent resonance structure(s) - empty box)
```
```
O O
/ \ // \
CH2 \
| /
(double arrow showing first equilibrium process)
(first resonance structure - empty box)
(double arrow showing second equilibrium process)
(second resonance structure - empty box)
```
#### pKa Values
**a)** For Compound A:
```
pKa: (empty box for student input)
```
**b)** For Compound B:
```
pKa: (empty box for student input)
```
#### Discussion
**c)** Explain their difference in pKa:
(Empty line for detailed answer)
The difference in pKa can be attributed to the nature and number of electron-withdrawing groups adjacent to the α-hydrogen. For Compound A, the presence of one carbonyl group impacts the acidity, while for Compound B, the presence of two carbonyl groups significantly increases the withdrawal effect, resulting in a different pKa value.
---
#### Conclusion
This exercise demonstrates the importance of structural features on the acidity of compounds and helps in understanding fundamental concepts of organic chemistry, specifically regarding the electron-withdrawing effects of carbonyl groups on adjacent hydrogens.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F30c2e2f2-e45c-41de-86ef-a25e36084e76%2Fca9fd8dc-0025-4c5f-926d-36e6dca50a87%2Fxja76f.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Identifying pKa Values of α-Hydrogen in Compounds
#### Introduction
Determining the pKa values of α-hydrogens in various compounds is important in understanding their acidity. Here, we will analyze the pKa values on a scale of 5 of the α-hydrogen in two compounds labeled as A and B, and then explain their differences.
#### Structures and pKa Values
**Compound A:**

Figure A shows a cyclic ketone with the molecular formula C₅H₈O. The α-hydrogen is located on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group.
**Compound B:**

Figure B shows a cyclic dione with the molecular formula C₆H₈O₂. The α-hydrogen is located on the carbon adjacent to two carbonyl groups.
Both compounds have their structures represented with equilibrium arrows indicating the deprotonation process:
```
O
/ \
CH2 \
| /
(double arrow showing equilibrium process)
(first compound's equivalent resonance structure(s) - empty box)
```
```
O O
/ \ // \
CH2 \
| /
(double arrow showing first equilibrium process)
(first resonance structure - empty box)
(double arrow showing second equilibrium process)
(second resonance structure - empty box)
```
#### pKa Values
**a)** For Compound A:
```
pKa: (empty box for student input)
```
**b)** For Compound B:
```
pKa: (empty box for student input)
```
#### Discussion
**c)** Explain their difference in pKa:
(Empty line for detailed answer)
The difference in pKa can be attributed to the nature and number of electron-withdrawing groups adjacent to the α-hydrogen. For Compound A, the presence of one carbonyl group impacts the acidity, while for Compound B, the presence of two carbonyl groups significantly increases the withdrawal effect, resulting in a different pKa value.
---
#### Conclusion
This exercise demonstrates the importance of structural features on the acidity of compounds and helps in understanding fundamental concepts of organic chemistry, specifically regarding the electron-withdrawing effects of carbonyl groups on adjacent hydrogens.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step 2
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY