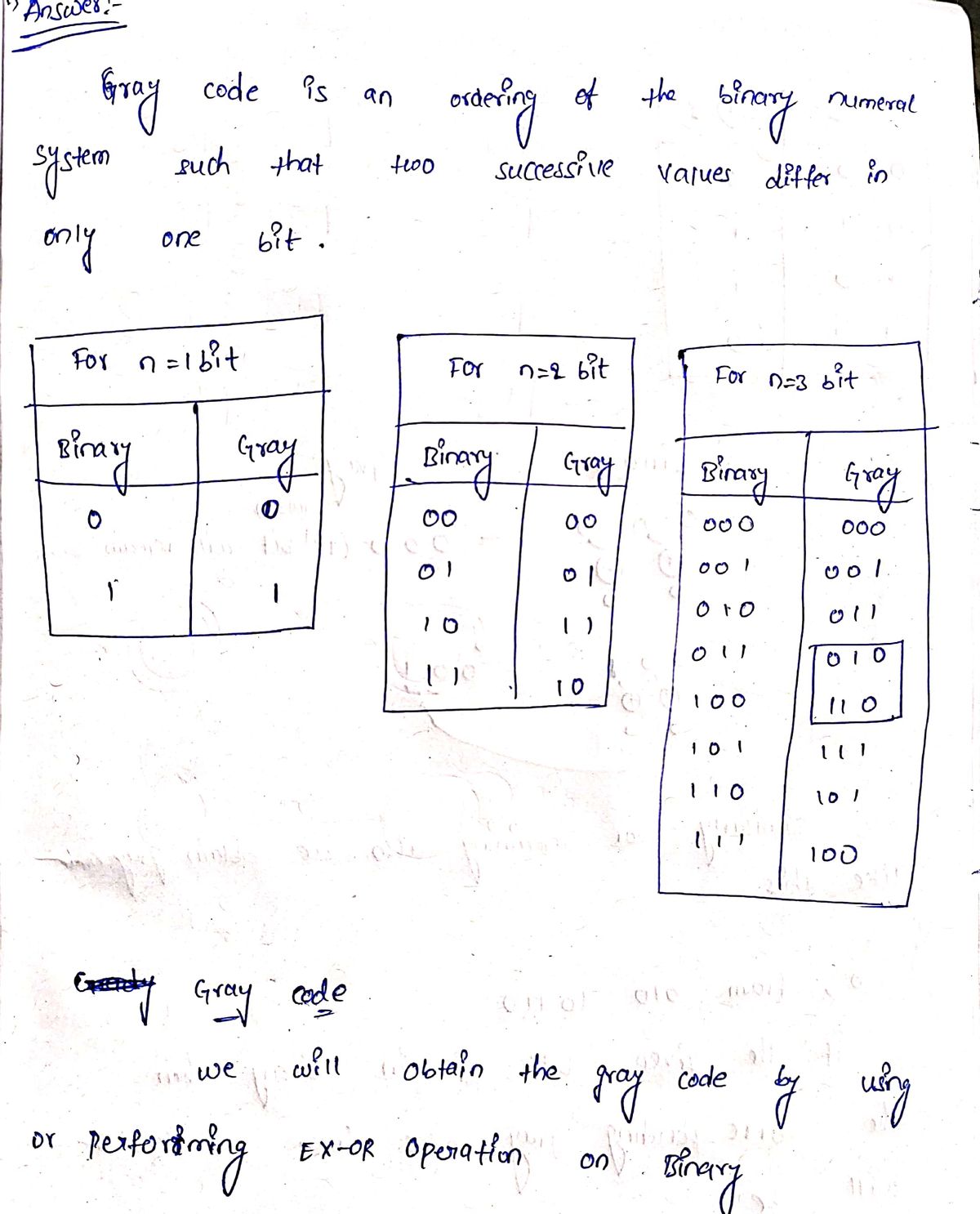
### Gray Code Generation Provide the Gray code of order 3 starting from 010 and ending at 110. **Explanation of Gray Code:** Gray Code, also known as Reflected Binary Code, is a binary numbering system where two successive values differ in only one bit. This property is especially useful in error correction in digital communications and minimizing the errors in analog to digital conversions. Here's how you can generate Gray codes for a given order: 1. **Identify the Order**: The order of the Gray code refers to the number of binary digits involved. An order of 3 means you have three binary digits. 2. **Generate Sequence**: - Start with the binary representation of the number you begin with, in this case, 010. - Identify the next number where only one bit changes from the previous number. - Continue this process until you reach the target ending binary sequence, here, 110. **Example of a Gray Code Sequence (Order 3):** - 000 - 001 - 011 - 010 - 110 - 111 - 101 - 100 Use Gray codes for tasks where reducing error and maintaining synchronization in digital communications are priorities.
### Gray Code Generation Provide the Gray code of order 3 starting from 010 and ending at 110. **Explanation of Gray Code:** Gray Code, also known as Reflected Binary Code, is a binary numbering system where two successive values differ in only one bit. This property is especially useful in error correction in digital communications and minimizing the errors in analog to digital conversions. Here's how you can generate Gray codes for a given order: 1. **Identify the Order**: The order of the Gray code refers to the number of binary digits involved. An order of 3 means you have three binary digits. 2. **Generate Sequence**: - Start with the binary representation of the number you begin with, in this case, 010. - Identify the next number where only one bit changes from the previous number. - Continue this process until you reach the target ending binary sequence, here, 110. **Example of a Gray Code Sequence (Order 3):** - 000 - 001 - 011 - 010 - 110 - 111 - 101 - 100 Use Gray codes for tasks where reducing error and maintaining synchronization in digital communications are priorities.
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:### Gray Code Generation
Provide the Gray code of order 3 starting from 010 and ending at 110.
**Explanation of Gray Code:**
Gray Code, also known as Reflected Binary Code, is a binary numbering system where two successive values differ in only one bit. This property is especially useful in error correction in digital communications and minimizing the errors in analog to digital conversions.
Here's how you can generate Gray codes for a given order:
1. **Identify the Order**: The order of the Gray code refers to the number of binary digits involved. An order of 3 means you have three binary digits.
2. **Generate Sequence**:
- Start with the binary representation of the number you begin with, in this case, 010.
- Identify the next number where only one bit changes from the previous number.
- Continue this process until you reach the target ending binary sequence, here, 110.
**Example of a Gray Code Sequence (Order 3):**
- 000
- 001
- 011
- 010
- 110
- 111
- 101
- 100
Use Gray codes for tasks where reducing error and maintaining synchronization in digital communications are priorities.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY