Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Please name the structures, any help with this would be great!

Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the chemical structure of ethyl benzoate, an organic compound. Ethyl benzoate is an ester formed from the reaction of benzoic acid and ethanol.
### Detailed Structure Explanation:
1. **Benzene Ring**: On the right side is a six-carbon benzene ring, characterized by alternating double bonds.
2. **Ester Group**: Connected to the benzene ring is an ester functional group, characterized by the carbonyl group (C=O) adjacent to an oxygen atom bonded to another carbon.
3. **Ethyl Chain**: Extending from the ester group is an ethyl chain (-CH2CH3), which completes the structure of ethyl benzoate.
### Notes:
- **Usage**: Ethyl benzoate is commonly used as a flavoring agent due to its fruity aroma.
- **Properties**: It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant scent, often found in various fruits.
This structure is useful for educational purposes in organic chemistry, highlighting the configuration and components of ester compounds.

Transcribed Image Text:This image shows the chemical structure of Valeramide.
### Description
**Chemical Formula:** C5H11NO
**Structure Details:**
- The molecule consists of a five-carbon chain.
- The sequence begins with an amide group, indicated by the presence of an NH2 (amine group) bonded to a carbon that is double-bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group).
- This carbonyl carbon is bonded to the first carbon in the chain which continues with three additional carbon atoms forming a straight chain, ending with a terminal carbon.
**Functional Groups:**
- **Amide Group:** Part of the structure, contributing to the chemical reactivity and properties of the molecule.
- **Alkyl Chain:** The linear chain of carbon atoms (three CH2 groups followed by a CH3 group), which can affect the compound's physical properties such as solubility and melting point.
### Applications
Valeramide can be studied as part of organic chemistry courses to understand amide functional groups and their chemical behavior. It may also be explored in contexts involving structural organic chemistry and synthesis.
Expert Solution
Step 1
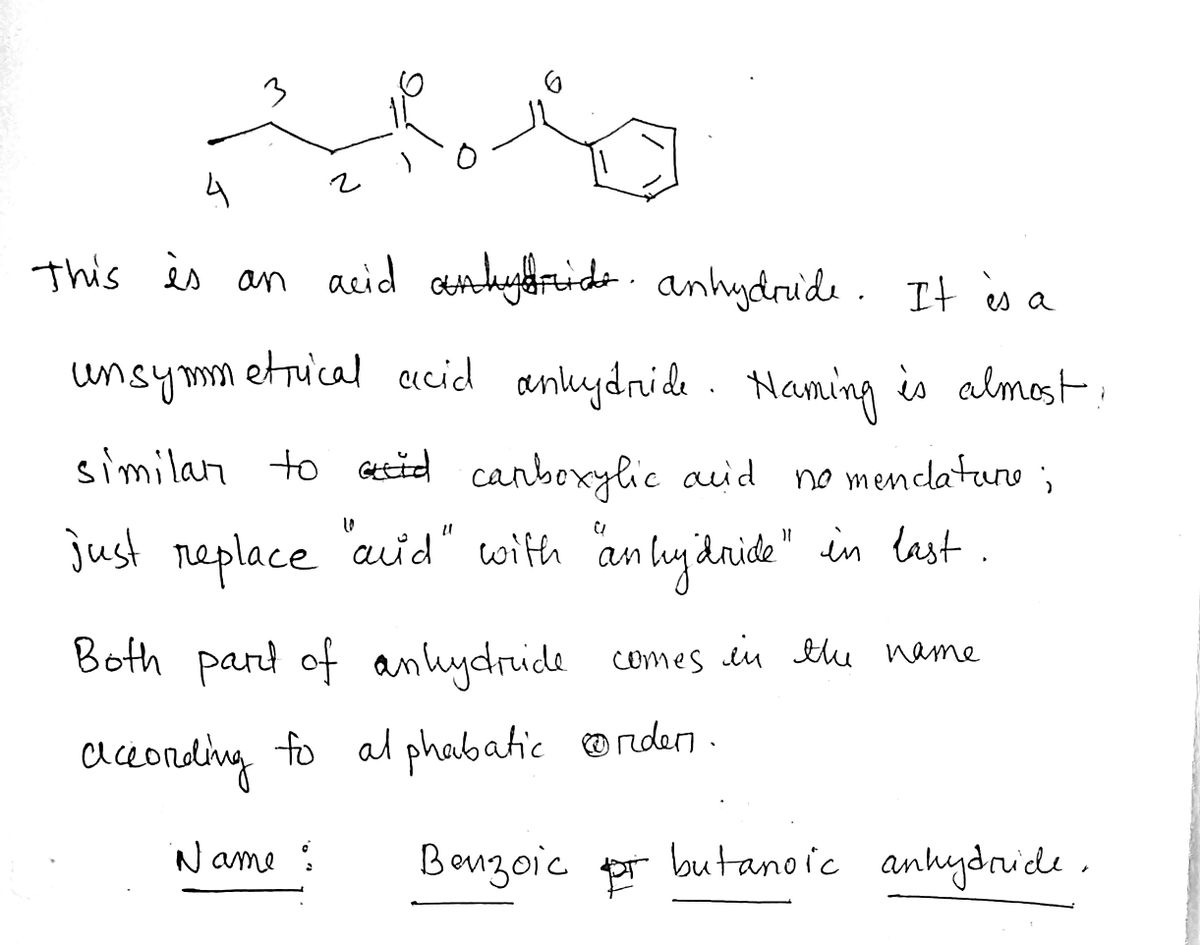
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY