One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 400,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.02 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $10 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.04 per unit for wages plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.009 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house at a rate of 100 percent of direct labor wage costs. The firm uses a cost of capital of 14 percent per year. a. Calculate the difference in NPVs between the Make and Buy options. Express all costs as positive values in your calculations. It is suggested to use the NPV function in Excel. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Difference in NPV b. Should you continue to produce in-house or accept the bid from your Taiwanese supplier?
One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 400,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.02 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $10 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.04 per unit for wages plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.009 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house at a rate of 100 percent of direct labor wage costs. The firm uses a cost of capital of 14 percent per year. a. Calculate the difference in NPVs between the Make and Buy options. Express all costs as positive values in your calculations. It is suggested to use the NPV function in Excel. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Difference in NPV b. Should you continue to produce in-house or accept the bid from your Taiwanese supplier?
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Chapter1: Investments: Background And Issues
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PS
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 16-11 (Algo)
One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The
supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 400,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3.
Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.02 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should
amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $10 per month.
Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would
cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.04 per unit for wages plus a 50
percent surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.009 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and
design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house at a
rate of 100 percent of direct labor wage costs. The firm uses a cost of capital of 14 percent per year.
a. Calculate the difference in NPVs between the Make and Buy options. Express all costs as positive values in your calculations. It is
suggested to use the NPV function in Excel. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Difference in NPV
b. Should you continue to produce in-house or accept the bid from your Taiwanese supplier?
Accept the bid
O Produce in-house
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
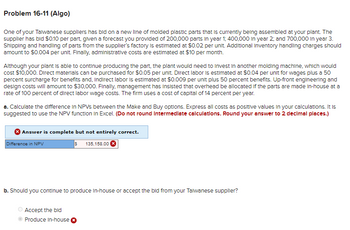
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 16-11 (Algo)
One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The
supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 400,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3.
Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.02 per unit. Additional Inventory handling charges should
amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $10 per month.
Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would
cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.04 per unit for wages plus a 50
percent surcharge for benefits and, Indirect labor is estimated at $0.009 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and
design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house at a
rate of 100 percent of direct labor wage costs. The firm uses a cost of capital of 14 percent per year.
a. Calculate the difference in NPVs between the Make and Buy options. Express all costs as positive values in your calculations. It is
suggested to use the NPV function in Excel. (Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
$ 135,158.00
Difference in NPV
b. Should you continue to produce in-house or accept the bid from your Taiwanese supplier?
Accept the bld
Produce In-house
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:
9781260013924
Author:
Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,



Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:
9781260013924
Author:
Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:
9780134897264
Author:
KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:
Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395250
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i…
Finance
ISBN:
9780077861759
Author:
Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education