Objective: Use the Chi Square test to determine whether you can reject a hypothesis about inheritance. 3. An RRYY yellow, round pea was crossed with a rryy green, wrinkled pea. All of the F1 peas were yellow and round. Two of the F1 peas (RrYy) were crossed to get the F2 generation shown below: 315 yellow, round 101 yellow, wrinkled 108 green, round 32 green, wrinkled A) How many degrees of freedom are there in the F2 generation? B) How many yellow, wrinkled peas would you expect from this cross? Write the calculation below. C) Calculate the expected for all of the phenotypic classes. Your null hypothesis is that your observed ratio is NOT DIFFERENT from the expected ratio. Phenotype Observed Expected (o-e)^2/e Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled Green, round Green, wrinkled D) Calculate the Chi square value and fill it in the table E) Add the chi square values together. X²= F) What is the p value for this chi square statistic? Chi Square Values and Probability Degrees of Freedom 1 2 3 4 5 P = 0.99 0.000157 0.020 0.115 0.297 0.554 0.95 0.00393 0.103 0.352 0.711 1.145 0.80 0.0642 0.446 1.005 1.649 2.343 0.50 0.455 1.386 2.366 3.357 4.351 0.20 1.642 3.219 4.642 5.989 7.289 0.05 3.841 5.991 7.815 9.488 11.070 0.01 6.635 9.210 11.345 13.277 15.086
Objective: Use the Chi Square test to determine whether you can reject a hypothesis about inheritance. 3. An RRYY yellow, round pea was crossed with a rryy green, wrinkled pea. All of the F1 peas were yellow and round. Two of the F1 peas (RrYy) were crossed to get the F2 generation shown below: 315 yellow, round 101 yellow, wrinkled 108 green, round 32 green, wrinkled A) How many degrees of freedom are there in the F2 generation? B) How many yellow, wrinkled peas would you expect from this cross? Write the calculation below. C) Calculate the expected for all of the phenotypic classes. Your null hypothesis is that your observed ratio is NOT DIFFERENT from the expected ratio. Phenotype Observed Expected (o-e)^2/e Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled Green, round Green, wrinkled D) Calculate the Chi square value and fill it in the table E) Add the chi square values together. X²= F) What is the p value for this chi square statistic? Chi Square Values and Probability Degrees of Freedom 1 2 3 4 5 P = 0.99 0.000157 0.020 0.115 0.297 0.554 0.95 0.00393 0.103 0.352 0.711 1.145 0.80 0.0642 0.446 1.005 1.649 2.343 0.50 0.455 1.386 2.366 3.357 4.351 0.20 1.642 3.219 4.642 5.989 7.289 0.05 3.841 5.991 7.815 9.488 11.070 0.01 6.635 9.210 11.345 13.277 15.086
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Class 16 Activity: Dihybrid Crosses and Chi Square Analysis
Objective: connect crosses using multiple genes to Punnett squares and probability
1. A green wrinkled pea plant is crossed with a round, yellow pea plant (RRYY). All the F1 peas are round and yellow
(RrYy). Consider meiosis for these RrYy plants.
A) If the chromosomes have lined up as shown below in meiosis I, what gametes will the RrYy pea plant produce?
RR rr
YY yy
B) Draw the other way the chromosomes could line up. What gametes would be made in this case?
C) Considering BOTH possible alignments, what are all the possible gametes and their frequencies?
2. Make a Punnett square for a cross between two round yellow peas with the genotype RrYy (a dihybrid cross).
What is the probability of producing a round, green pea?
What is the probability of producing a round, green pea OR a round, yellow pea?

Transcribed Image Text:Objective: Use the Chi Square test to determine whether you can reject a hypothesis about inheritance.
3. An RRYY yellow, round pea was crossed with a rryy green, wrinkled pea. All of the F1 peas were yellow and round.
Two of the F1 peas (RrYy) were crossed to get the F2 generation shown below:
315 yellow, round
101 yellow, wrinkled
108 green, round
32 green, wrinkled
A) How many degrees of freedom are there in the F2 generation?
B) How many yellow, wrinkled peas would you expect from this cross? Write the calculation below.
C) Calculate the expected for all of the phenotypic classes.
Your null hypothesis is that your observed ratio is NOT DIFFERENT from the expected ratio.
Phenotype
Observed
Expected
(o-e)^2/e
Yellow, round
Yellow, wrinkled
Green, round
Green, wrinkled
D) Calculate the Chi square value and fill it in the table
E) Add the chi square values together. X²=
F) What is the p value for this chi square statistic?
Chi Square Values and Probability
Degrees of
Freedom
1
2
3
4
5
P = 0.99
0.000157
0.020
0.115
0.297
0.554
0.95
0.00393
0.103
0.352
0.711
1.145
0.80
0.0642
0.446
1.005
1.649
2.343
Reject the null hypothesis
Differences are due to chance
0.50
0.455
1.386
2.366
3.357
4.351
0.20
1.642
3.219
4.642
5.989
7.289
0.05
3.841
5.991
7.815
9.488
11.070
G) What conclusions can you make from these data? Check the correct answers.
Don't reject the null hypothesis
Differences are not due to chance
0.01
6.635
9.210
11.345
13.277
15.086
Expert Solution
Question 1.A
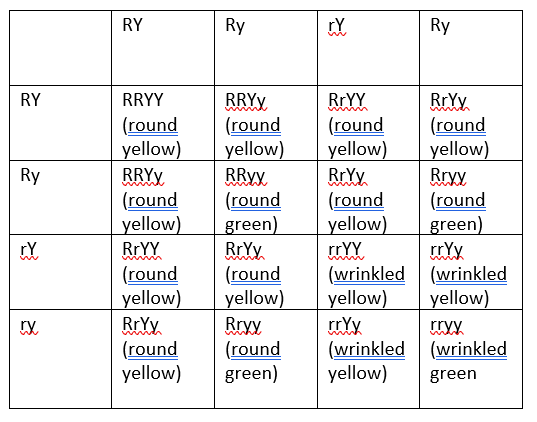
Probablity of producing round green pea is 3/16 and
Probablity of producing round yellow pea is 9/16.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education