Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
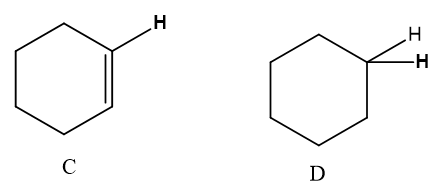
For each pair of compounds: [1] Which indicated H is more acidic? [2] Draw the conjugate base of each acid. [3] Which conjugate base is stronger?


For each pair of compounds:
1. Which indicated H is more acidic?
2. Draw the conjugate base of each acid.
3. Which conjugate base is stronger?
Given compounds,
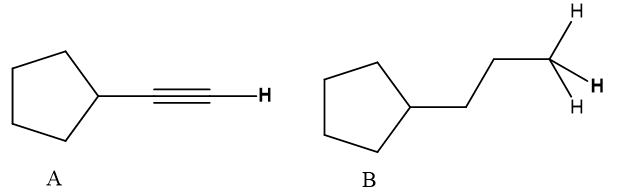

(1) The H in An is attached to sp hybridized C iota though H in B is clung to sp3 hybridized C particle. As the s character of C to which H is reinforced gets expands the acridity additionally increments. Hence, the featured H molecule is given that compound A will be more acidic than the featured H in compound B.
(2) A corrosive loses one proton, at that point, the shaped species is known as a formed base. The form base of each given corrosive is as per the following,
,
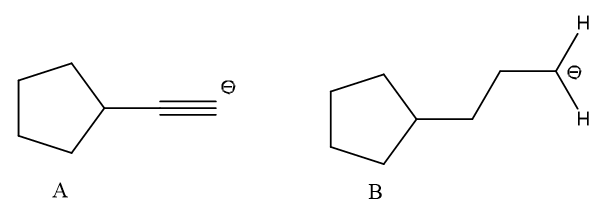
(3) For the most part, more grounded corrosive creates a more vulnerable form base and frail corrosive structures a solid form base. Subsequently, the design of a solid form base is as per the following,
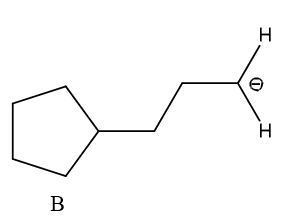
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 8 images









