Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

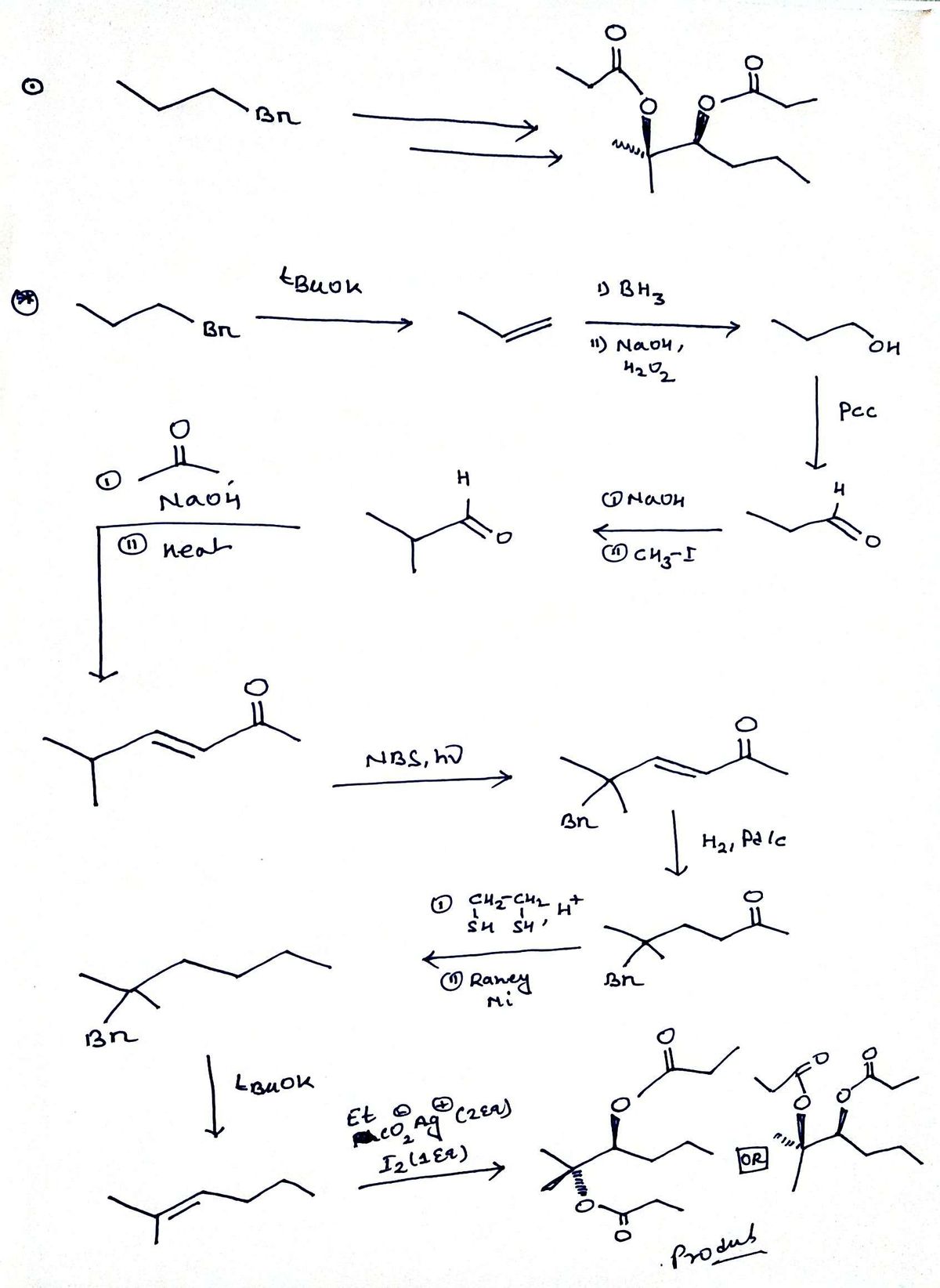
Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a chemical reaction transformation starting from 1-bromopropane to a more complex organic molecule.
On the left side of the diagram, 1-bromopropane is illustrated by a straight chain of three carbon atoms, with a bromine (Br) atom attached to the terminal carbon. An arrow points from 1-bromopropane to the product on the right.
The product on the right of the arrow is a more complex organic molecule featuring two ester functional groups (RCOOR'). The structure consists of a chain of seven carbon atoms. Starting from the left, there is an ester linkage (–C(=O)O–) with a carbonyl group adjacent to it. The center carbon atom in the chain exhibits stereochemistry, indicated by the wedge-and-dash notation. Another ester group is present mid-structure, and the chain terminates with two additional carbon atoms bonded to a carbonyl group each.
Overall, the diagram depicts a conversion of a simple alkyl halide into a more complex molecule containing multiple functionality and stereochemical features.

Transcribed Image Text:This image presents a flowchart depicting a series of organic chemical reactions involving various functional groups. The diagram includes starting materials, intermediates, and final products, along with reagents and conditions required for each transformation.
**Reaction Pathways:**
1. **Path A:**
- Starts with an alcohol (R–OH).
- Converts to a carboxylic acid (R–COOH).
2. **Path B:**
- Begins with a carboxylic acid (R–COOH).
- Proceeds through an acid-catalyzed hydration step involving H₃O⁺.
- Results in an alcohol (R–OH).
3. **Path C:**
- Carboxylic acid (R–COOH) reacts with NaOH followed by CH₃CH₂I.
- Forms an ester (RCOOCH₂CH₃).
4. **Path D:**
- Carboxylic acid (R–COOH) is converted to an acid chloride (R–COCl).
5. **Path E:**
- Acid chloride (R–COCl) undergoes reaction to form an amide (R–CONH₂).
6. **Path F:**
- Amide (R–CONH₂) undergoes further reaction.
- Produces a secondary amine (R–NH–CH₃).
7. **Path G:**
- Involves a different transformation pathway starting from a diester compound.
- No specific reagents detailed for this transformation in the image.
This diagram serves as a guide for understanding the conversion between different organic compounds using specific reagents, showcasing principles of organic synthesis.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY