Methane (CH₂) gas and oxygen (O₂) gas react to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas and water (H₂O) vapor. Suppose you have 13.0 mol of CH4 and 11.0 mol of O₂ in a reactor. Calculate the largest amount of CO₂ that could be produced. Round your answer to the nearest 0.1 mol. mol X obb A
Methane (CH₂) gas and oxygen (O₂) gas react to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas and water (H₂O) vapor. Suppose you have 13.0 mol of CH4 and 11.0 mol of O₂ in a reactor. Calculate the largest amount of CO₂ that could be produced. Round your answer to the nearest 0.1 mol. mol X obb A
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Can you solve it and give me the answer
![**Title: Solving Moles-to-Moles Limiting Reactant Problems**
**Section: Chemical Reactions**
**Problem:**
Methane (\(CH_4\)) gas and oxygen (\(O_2\)) gas react to form carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) gas and water (\(H_2O\)) vapor. Suppose you have 13.0 mol of \(CH_4\) and 11.0 mol of \(O_2\) in a reactor.
Calculate the largest amount of \(CO_2\) that could be produced. Round your answer to the nearest 0.1 mol.
**Input Box:**
- Enter your answer in the provided box labeled "mol."
**Buttons:**
- **Explanation**: Provides detailed steps for solving the problem.
- **Check**: Verifies your answer.
**Additional Information:**
This problem involves identifying the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction and using stoichiometry to calculate the maximum possible amount of product formed. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
\[ \text{CH}_4 + 2\text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{CO}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \]
Knowing the reactant quantities and using stoichiometry is essential to finding the limiting reactant and determining the correct yield of \(CO_2\).
**Note:**
- This problem is part of a practice exercise aimed at strengthening understanding of stoichiometric calculations and limiting reactant concepts.
- Make sure to consult the explanation section for step-by-step guidance if needed.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ffc5d9ab7-5262-4222-989c-d8b3bd159f6f%2F3f468123-cb87-44d6-b830-c346f7a16613%2Ffl7ta8q_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Solving Moles-to-Moles Limiting Reactant Problems**
**Section: Chemical Reactions**
**Problem:**
Methane (\(CH_4\)) gas and oxygen (\(O_2\)) gas react to form carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) gas and water (\(H_2O\)) vapor. Suppose you have 13.0 mol of \(CH_4\) and 11.0 mol of \(O_2\) in a reactor.
Calculate the largest amount of \(CO_2\) that could be produced. Round your answer to the nearest 0.1 mol.
**Input Box:**
- Enter your answer in the provided box labeled "mol."
**Buttons:**
- **Explanation**: Provides detailed steps for solving the problem.
- **Check**: Verifies your answer.
**Additional Information:**
This problem involves identifying the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction and using stoichiometry to calculate the maximum possible amount of product formed. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
\[ \text{CH}_4 + 2\text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{CO}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \]
Knowing the reactant quantities and using stoichiometry is essential to finding the limiting reactant and determining the correct yield of \(CO_2\).
**Note:**
- This problem is part of a practice exercise aimed at strengthening understanding of stoichiometric calculations and limiting reactant concepts.
- Make sure to consult the explanation section for step-by-step guidance if needed.
Expert Solution
Step 1
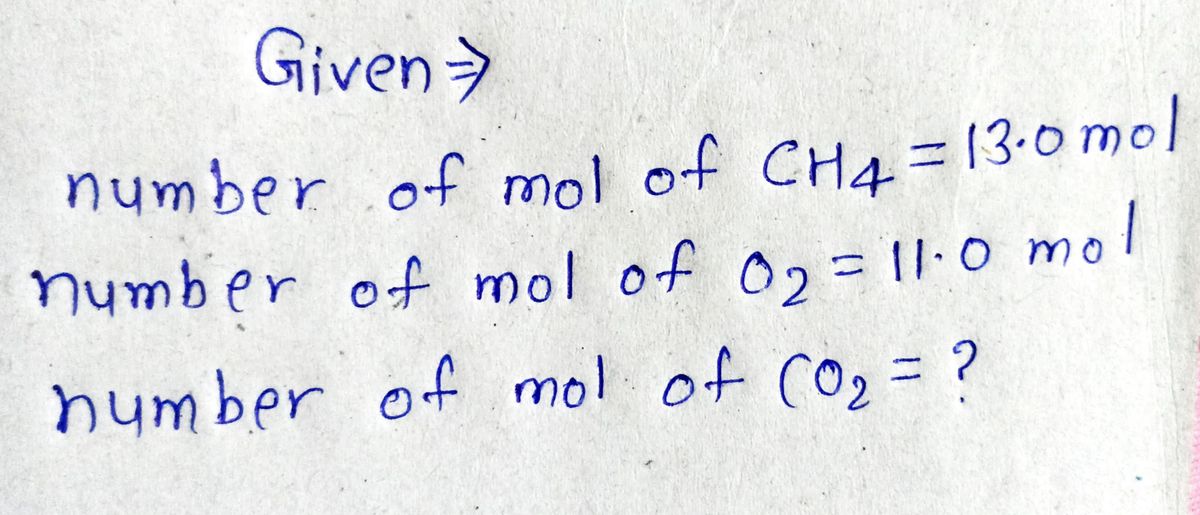
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY