M m رے 0
Q: The 7-kg sphere is projected horizontally with a velocity of 19 m/s against the 35-kg carriage which…
A: Here mass of the sphere m1=7 kg Velocity v1=19 m/s mass of the carriage m2=35 kg Velocity after…
Q: need help on the question in the picture
A: Using conservation of momentum along x direction,
Q: Problem 1 (Pro 3.13 Textbook modified): Using the method of joints, determine the force in members…
A: For calculation consider L = 1
Q: 8) Calculate the magnitude of the buoyant force acting on the boat if it were entirely submerged…
A:
Q: Dynamics of a system can be divided into kinematics and kinetics. To analyse the dynamic of the…
A: Kinetics and Kinematics are two different branches of physics, however, one may confuse the two to…
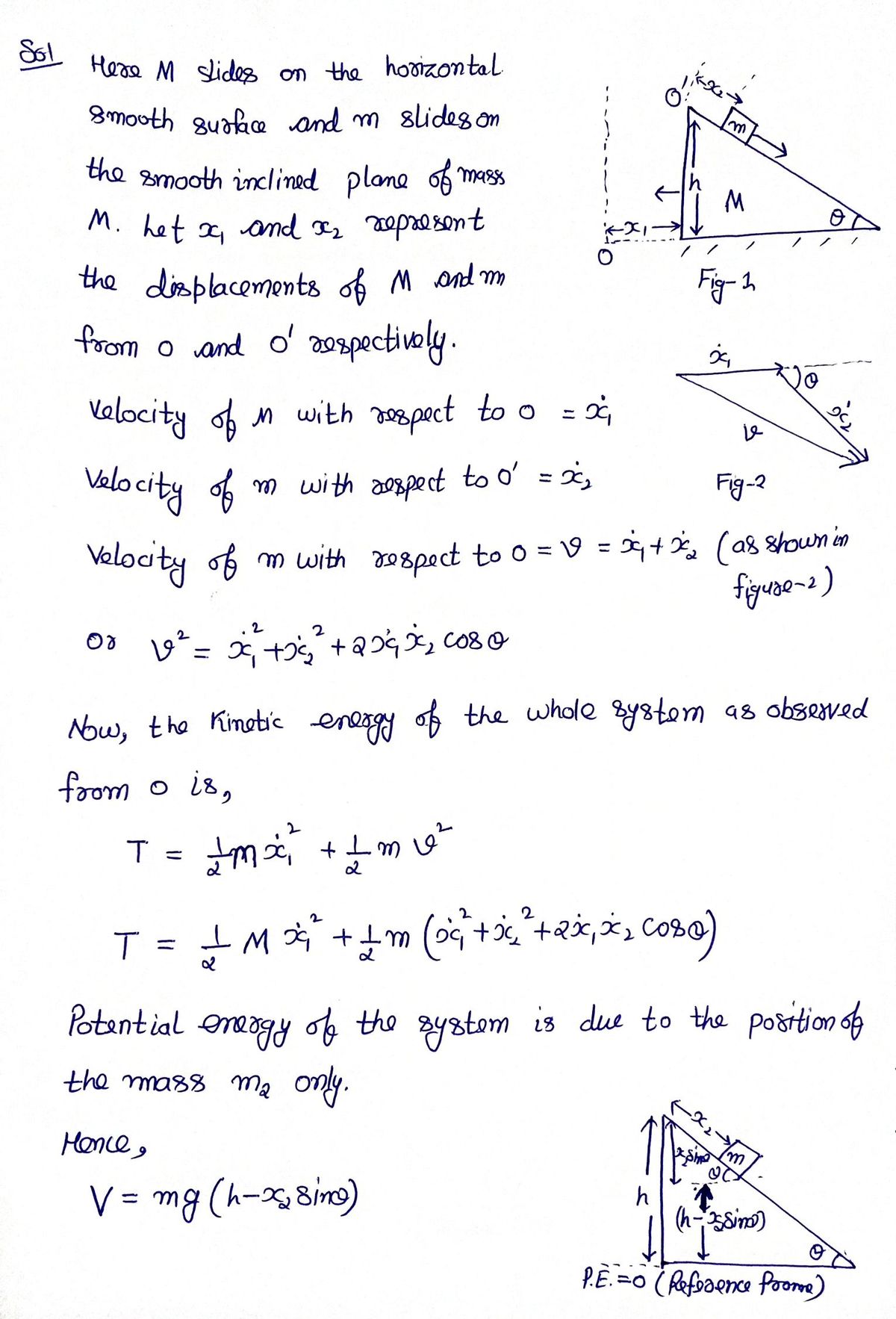
Q: Use Lagrangian formalism to solve the following problem: A block of mass m is held motionless on a…
A: Given data: mass of block=m, mass of plane=M, the angle of inclination=θ, a) change in vertical…
Q: らKN ちm
A:
Q: A solid disc of radius. 10 m is mounted on the vertical axis. A string of negligible masses wrapped…
A: When a force is applied on a moving object in the direction of the object, then there causes…
Q: Knowing the connection between velocity and kinetic energy, make a sketch of the system below, and…
A: Answer: The velocity v and the kinetic energy KE are related to each other by the following…
Q: 1. A 300 lbm block is initially at rest on a flat surface that is inclined at 30 deg. If the…
A:
Q: Why is Newton's cradle (Newton's balls) described as an "almost-ideal" closed system? Explain your…
A: Newton's cradle or Newton's balls,When one of the balls is lifted and released, it strikes the…
Q: The force that attracts an apple towards the earth is the same that attract Earth towards the apple…
A: Note:- Since you have asked multiple question, we will solve the first question for you. If you want…
Q: 7-5. Consider a vertical plane in a constant gravitational field. Let the origin of a coor- dinate…
A:
Q: A block of mass m that slides frictionlessly on an inclined plane as shown in the figure
A: Block of mass m that slides frictionlessly on an inclined plane as shown in the figure.
Q: QM An object of mass M is attached to a string. The length of the string is r and has no mass. The…
A:
Determine the motion expressions for each of the systems shown below by using the Euler-Lagrange equation.
not skiping steps please explain i do not understand yet
A block of mass m that slides without friction on a triangular-side wedge which moves to the left (without friction) while the block lowers on the inclined plane as shown in the figure

Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

- Obtain the Lagrangian equations of the PR(prismatic+rotarary) manipulator in the figure. write in vector form. (use the kinetic and potential energy,angular and lineer velecoties-h-m1-m2-I1-I2-w for finding lagrange equations) I want to see how the kinetic and potential energies obtained for each link are found. (do not copy the answer from another answered question)GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING Given: A 10-kg block is subjected to a force F=500 N. A spring of stiffness k=500 N/m is mounted F = 500 N against the block. When s = 0, the block is at rest and the spring is k = 500 N/m ssed. The contact surface uncomp is smooth. Find: Draw the free-body and kinetic diagrams of the block. Plan: 1) Define an inertial coordinate system. 2) Draw the block's free-body diagram, showing all external forces applied to the block in the proper directions. 3) Draw the block's kinetic diagram, showing the inertial force vector ma in the proper direction. ALWAYS LEARNING Dynamics, Fourteenth Edition in SI Units R.C. Hibbeler Copyright ©2017 by Pearson Education, Ltd. PEAR SON All rights reserve 21Initially, the system of objects shown in the figure below is held motionless. The pulley and all surfaces are frictionless. Let the force F be zero and assume that m, can move only vertically (with respect to the ground). At the instant after the system of objects is released, find each of the following. (Note: The pulley accelerates along with object M. Use the following as necessary: m₁, m₂, M, and g, where g is the magnitude of the gravitational acceleration. Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only. Take the rightward and upward directions to be positive. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) (a) the tension 7 in the string T= M (b) the acceleration of m₂ am₂= (c) the acceleration of M ³M™ (d) the acceleration of m amy vertical
- Disclaimer: if this problem is chosen for the mini-exam, the given function may be different, but will be chosen from the exponential, trigonometric, or polynomial families. * There are two particles (1 and 2) that are moving around in space. The mass of particle 1 is m1 and the mass of particle 2 is m2. The particles are isolated so that only the forces between the particles are significant. The force that 2 exerts on 1 is given by: 2. F1(t) = Fo e î + sin where F, and t, are both constants. The particles interact with one another from t = 0 until t = t1. a. What is the physical meaning of F,? b. Find the impulse from particle 1 on particle 2 over this time interval. c. Find the impulse from particle 2 on particle 1 over this time interval. d. Find the change in momentum of particle 1 over this time interval. e. Find the change in momentum of particle 2 over this time interval. f. Find the change in momentum of the system that consists of particle 1 and particle 2 over this time…Theoretical Mechanics Topic: Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics >Generate the necessary equations to this system. > Use the equations of motion >Generate equations for (x,y), (Vx,Vy), V², T > L = T-U --- For study purposes. Thank you!A small box is being launched along a track as shown below (if the image does not load, click here). From A to E the track is smooth whereas it is rough from E to F with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.53. The segment B-C-D is a circular section with a radius of 3.1 m. The table below summarises some relevant information. At A, the block is at rest and the spring is unstretched. Values h1 = 0.49 m h2 = 1.2m Track.png Calculate the maximum speed of the block at C before losing contact with the track. For that maximum speed, calculate the required distance d for the block to stop at F. Write your answer to d in millimetres rounded to the nearest millimetre. (previous answers to similar questions on this site are incorrect)