Let's look back at the Quetsion #4 where one fluid had convection coefficient of 100 150 W/m².K. Let's consider that we change the second fluid such that its convection coeffient become twice of what it was in Quetsion #4 of HW#4. The first fluid is the hot fluid which comes in at 78°C and exits at 62°C. The second fluid (i.e., the cold fluid) enters the heat exchanger at 35°C and exits at 67°C. Let us also consider that this is a concentric-tube heat exchanger. (a) Look at the inlet and outlet temperatures and explain if this is a counter-flow or a parallel-flow heat exchanger. (b) What is the overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger? (c) The heat capacity rate of the hot fluid was found to be 1080 W/°C. If the cold fluid is water (with a specific heat of 4180 J/kg-K), what is the required mass flow for the water? (d) What is the required heat transfer surface area?
Let's look back at the Quetsion #4 where one fluid had convection coefficient of 100 150 W/m².K. Let's consider that we change the second fluid such that its convection coeffient become twice of what it was in Quetsion #4 of HW#4. The first fluid is the hot fluid which comes in at 78°C and exits at 62°C. The second fluid (i.e., the cold fluid) enters the heat exchanger at 35°C and exits at 67°C. Let us also consider that this is a concentric-tube heat exchanger. (a) Look at the inlet and outlet temperatures and explain if this is a counter-flow or a parallel-flow heat exchanger. (b) What is the overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger? (c) The heat capacity rate of the hot fluid was found to be 1080 W/°C. If the cold fluid is water (with a specific heat of 4180 J/kg-K), what is the required mass flow for the water? (d) What is the required heat transfer surface area?
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
DONT DO PROBLEM 4 it just here for reference. DO THE OTHER PROBLEM.

Transcribed Image Text:Let's look back at the Quetsion #4
where one fluid had convection coefficient of
100 150 W/m2.K. Let's consider that we change the second fluid such that its convection coeffient
become twice of what it was in Quetsion #4 of HW#4. The first fluid is the hot fluid which comes
in at 78°C and exits at 62°C. The second fluid (i.e., the cold fluid) enters the heat exchanger at
35°C and exits at 67°C. Let us also consider that this is a concentric-tube heat exchanger.
(a) Look at the inlet and outlet temperatures and explain if this is a counter-flow or a parallel-flow
heat exchanger.
(b) What is the overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger?
(c) The heat capacity rate of the hot fluid was found to be 1080 W/°C. If the cold fluid is water
(with a specific heat of 4180 J/kg-K), what is the required mass flow for the water?
(d) What is the required heat transfer surface area?

Transcribed Image Text:4. A heat exchanger is made of thin and conductive materials. It's overall heat transfer coefficient
was found to be 100 W/m².K. If the convection coefficient of one fluid is 150 W/m2.K, what is the
convection coefficient of the other fluid?
Expert Solution
Step 1
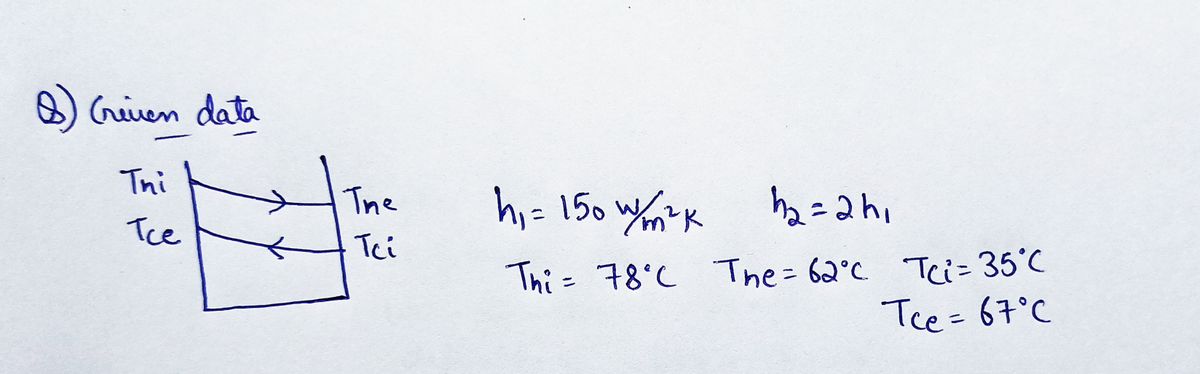
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY