is a version of an amide bond
Nucleotides
It is an organic molecule made up of three basic components- a nitrogenous base, phosphate,and pentose sugar. The nucleotides are important for metabolic reactions andthe formation of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules present in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and viruses. They carry the genetic information for the synthesis of proteins and cellular replication. The nucleic acids are of two types: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The structure of all proteins and ultimately every biomolecule and cellular component is a product of information encoded in the sequence of nucleic acids. Parts of a DNA molecule containing the information needed to synthesize a protein or an RNA are genes. Nucleic acids can store and transmit genetic information from one generation to the next, fundamental to any life form.
A peptide bond...
Proteins can function as structural elements (hair, wool, collagen), enzymes, hormones, hereditary factors, transcription factors, oxygen carriers etc.
Proteins are the polymers made up of monomeric units called amino acids. Hence, amino acids are known as building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid is a nitrogenous compound having acidic carboxyl group (-COOH known as C-Terminal) and the basic amino group (--NH2 Known as N-Terminal) group. R is a side chain that is different in each amino acid.
The general formula of an amino acid is
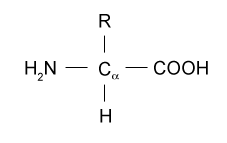
In a protein chain, adjacent amino acids are linked to each other through a special type of amide bond called a peptide bond leading to a primary structure of a protein. It is generally known as CO-NH linkage formed due to the elimination of a water molecule.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









