In a sales effectiveness seminar, a group of sales representatives tried two approaches to selling a customer a new automobile: the aggressive approach and the passive approach. For 1160 customers, the following record was kept: No Sale Row Total 580 Sale Aggressive 275 305 Passive 487 762 93 580 Column Total 398 1160 Suppose a customer is selected at random from the 1160 participating customers. Let us use the following notation for events: A = aggressive approach, Pa = passive approach, S = sale, N = no sale. So, P(A) is the probability that an aggressive approach was used, and so on. (a) Compute P(S), P(S | A), and P(S | Pa). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(S) = P(S | A) = P(S | Pa) = (b) Are the events S = sale and Pa = passive approach independent? Explain. O Yes. The two events can occur together. O No. The two events cannot occur together. O Yes. P(S) = P(S | Pa). O No. P(S) # P(S | Pa). (c) Compute P(A and S) and P(Pa and S). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(A and S) = P(Pa and S) = (d) Compute P(N) and P(N | A). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(N) =| P(N | A) = |
In a sales effectiveness seminar, a group of sales representatives tried two approaches to selling a customer a new automobile: the aggressive approach and the passive approach. For 1160 customers, the following record was kept: No Sale Row Total 580 Sale Aggressive 275 305 Passive 487 762 93 580 Column Total 398 1160 Suppose a customer is selected at random from the 1160 participating customers. Let us use the following notation for events: A = aggressive approach, Pa = passive approach, S = sale, N = no sale. So, P(A) is the probability that an aggressive approach was used, and so on. (a) Compute P(S), P(S | A), and P(S | Pa). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(S) = P(S | A) = P(S | Pa) = (b) Are the events S = sale and Pa = passive approach independent? Explain. O Yes. The two events can occur together. O No. The two events cannot occur together. O Yes. P(S) = P(S | Pa). O No. P(S) # P(S | Pa). (c) Compute P(A and S) and P(Pa and S). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(A and S) = P(Pa and S) = (d) Compute P(N) and P(N | A). (Enter your answers as fractions.) P(N) =| P(N | A) = |
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:In a sales effectiveness seminar, a group of sales representatives tried two approaches to selling a customer a new automobile: the aggressive approach and the passive
approach. For 1160 customers, the following record was kept:
Sale
No Sale
Row Total
Aggressive
275
305
580
Passive
487
93
580
Column Total
762
398
1160
Suppose a customer is selected at random from the 1160 participating customers. Let us use the following notation for events: A =
aggressive approach, Pa =
passive approach,
S =
sale, N = no sale. So, P(A) is the probability that an aggressive approach was used, and so on.
(a) Compute P(S), P(S | A), and P(S | Pa). (Enter your answers as fractions.)
P(S)
P(S | A) =
P(S | Pa)
(b) Are the events S = sale and Pa = passive approach independent? Explain.
Yes. The two events can occur together.
No. The two events cannot occur together.
Yes. P(S) = P(S | Pa).
No. P(S) + P(S | Pa).
(c) Compute P(A and S) and P(Pa and S). (Enter your answers as fractions.)
Р(A and S) -
%D
P(Pa and S) =
(d) Compute P(N) and P(N | A). (Enter your answers as fractions.)
P(N)
P(N | A) =
Expert Solution
bit a
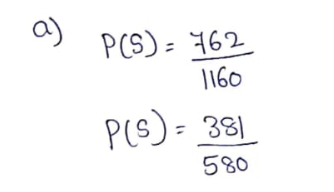
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
