Write a while loop that lets the user enter a number. The number should be multiplied by 10, and the result assigned to a variable named product. The loop should iterate as long as product is less than 100.
Types of Loop
Loops are the elements of programming in which a part of code is repeated a particular number of times. Loop executes the series of statements many times till the conditional statement becomes false.
Loops
Any task which is repeated more than one time is called a loop. Basically, loops can be divided into three types as while, do-while and for loop. There are so many programming languages like C, C++, JAVA, PYTHON, and many more where looping statements can be used for repetitive execution.
While Loop
Loop is a feature in the programming language. It helps us to execute a set of instructions regularly. The block of code executes until some conditions provided within that Loop are true.
Write a while loop that lets the user enter a number. The number should be multiplied
by 10, and the result assigned to a variable named product. The loop should iterate as
long as product is less than 100.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

I would like for the code in the attached image turned into a flow chart.
Thanks in advance!
![```python
import math
def isSquare(n):
sr = (int) (math.sqrt(n))
return (sr * sr == n)
def printPrimeAndFib(n):
prime =[True] * (n + 1)
p = 2
while(p * p <= n):
if (prime[p] == True):
for i in range(p * 2, n + 1, p):
prime[i] = False
p = p + 1
for i in range(2, n + 1):
if (prime[i] and (isSquare(5 * i * i + 4) > 0 or isSquare(5 * i * i - 4) > 0)):
print(i , " ",end="")
n = 233
printPrimeAndFib(n);
```
### Description
This Python script includes functions designed to identify and print numbers that are both prime and Fibonacci up to a given number `n`.
#### Functions
1. **isSquare(n)**
- Determines if a number `n` is a perfect square.
- Returns `True` if `n` is a perfect square, otherwise `False`.
2. **printPrimeAndFib(n)**
- Identifies prime numbers using the Sieve of Eratosthenes.
- Checks for Fibonacci numbers using the property that a number `x` is a Fibonacci number if one (or both) of `(5*x*x + 4)` or `(5*x*x - 4)` is a perfect square.
- Prints numbers that are both prime and Fibonacci within the range `2` to `n`.
#### Example
- Sets `n = 233` and calls `printPrimeAndFib(n)` to print all numbers up to 233 that are both prime and Fibonacci.
This script serves as an educational example for applying mathematical properties and concepts to solve a problem involving prime and Fibonacci numbers.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/a7e1b932-69d6-4780-b755-a77130ed504e/70f36788-d69e-4640-b0a1-86eabd6da7ce/iyw5k8e_thumbnail.png)
Design a loop (pick one you would like to use) that lets a user enter a number. Have the
*Does the flow chart in the attached image describe what is required in the above paragraph?*
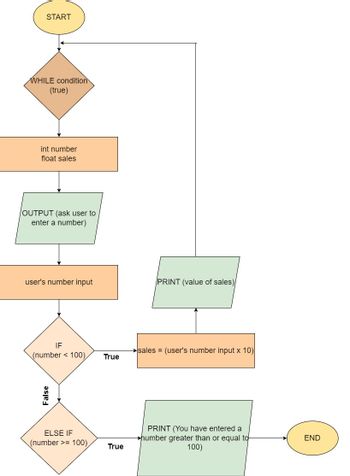
Design a loop (pick one you would like to use) that lets a user enter a number. Have the








