Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
100%
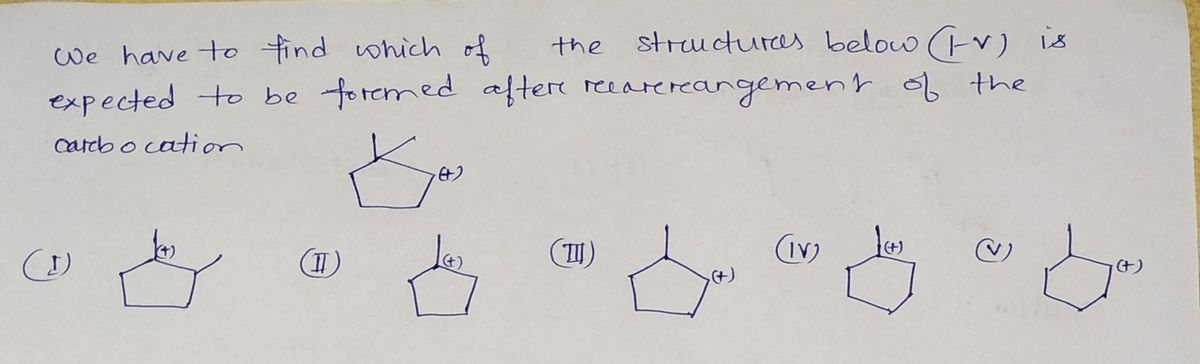
Which of the structures below (I-V) is expected to be formed after rearrangement of the following carbocation?

Transcribed Image Text:The image features a detailed diagram showing the structure of DNA. Below is the transcription and explanation of the diagram:
---
**DNA Structure: A Closer Look**
The DNA molecule is composed of two long strands forming a double helix, resembling a twisted ladder. Each strand is made up of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases, which pair specifically:
1. **Sugar-Phosphate Backbone:**
- Each strand of DNA consists of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. These form the structural framework of DNA.
2. **Nitrogenous Bases:**
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
3. **Base Pairing:**
- Adenine pairs with Thymine (A-T)
- Cytosine pairs with Guanine (C-G)
4. **Hydrogen Bonds:**
- The bases are paired through hydrogen bonds and opposite strands are held together by these pairs:
- A and T are connected by two hydrogen bonds.
- C and G are connected by three hydrogen bonds.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The spiral-shaped double helix is shown, emphasizing the complementary nature of base pairing.
- The phosphate-deoxyribose backbone is illustrated outside while the base pairs connect the two strands inside.
The precise pairing of the bases is crucial for DNA replication and function, ensuring the genetic information is accurately passed down through generations. Each sequence of DNA carries distinct genetic information, which codes for various proteins essential for life. Understanding this structure is fundamental to exploring genetic coding, mutations, and biotechnology applications.
---

Transcribed Image Text:The image is a chemical structure diagram representing a cyclopentyl carbocation. It consists of a five-membered carbon ring, known as a cyclopentane, with an additional carbon branch extending from one of the ring's carbon atoms. This additional carbon is attached to a positive charge, indicating it is a carbocation.
In this structure:
- The cyclopentane ring forms the base of the molecule.
- The branch from the ring leads to a positively charged carbon atom, which is a characteristic feature of carbocations, resulting in a highly reactive intermediate in many organic reactions.
Such diagrams are commonly used in organic chemistry to illustrate intermediate stages of chemical reactions, particularly in mechanisms involving rearrangements or substitutions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY