Formal Charges
Formal charges have an important role in organic chemistry since this concept helps us to know whether an atom in a molecule is neutral/bears a positive or negative charge. Even if some molecules are neutral, the atoms within that molecule need not be neutral atoms.
Polarity Of Water
In simple chemical terms, polarity refers to the separation of charges in a chemical species leading into formation of two polar ends which are positively charged end and negatively charged end. Polarity in any molecule occurs due to the differences in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Water, as we all know has two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom. As oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen thus, there exists polarity in the bonds which is why water is known as a polar solvent.
Valence Bond Theory Vbt
Valence bond theory (VBT) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. It gives a quantum mechanical approach to the formation of covalent bonds with the help of wavefunctions using attractive and repulsive energies when two atoms are brought from infinity to their internuclear distance.
How would you determine the order with respect to [S2O8^2-]?
![3.
4-
173
Table 12.2 Solutions for Kinetic Runs
Run
Flask A
Flask B
250 mL beaker
10.00 mL 0.00500 M NażS2O3
5 drops starch
20.00 mL 0.200 M KI
20.00 mL 0.100 M K2S2O8
10.00 mL 0.100 M K2S2O8
10.00 mL 0.100 M NażSO4
10.00 mL 0.00500 M Na2S2O3
5 drops starch
20.00 mL 0.200 M KI
15.00 mL 0.100 M K2S2O8
5.00 mL 0.100 M Na2SO4
10.00 mL 0.00500 M Na2S2O3
5 drops starch
20.00 mL 0.200 M KI
10.00 mL 0.200 M KI
10.00 mL 0.200 KCI
10.00 mL 0.00500 M Na2S2O3
20.00 mL 0.100 M K2S½O8
5 drops starch
15.00 mL 0.200 M KI
10.00 mL 0.00500 M Na2S2O3
20.00 mL 0.100 M K2S2O8
5.00 mL 0.200 M KCI
5 drops starch
For each of the above, measure the KI and the K2S½O8 precisely from the burets. The
KCl and Na2SO4 solutions are added only to keep the total ionic concentration in each
mixture the same. This is necessary to avoid secondary effects.
1. Calculate the initial concentrations of I, S,O2, and S,O, in each run using the data
in Table 12.2 and the dilution formula M¡V] = M2V2, is as follows:
-
(0.200 M)(20.00 mL)
=°[.1]
(50.00 mL)
-=0.0800 M
(0.100 M)(20.00 mL)
=0.0400 M
(50.00 mL)
(0.00500 M)(10.00 mL)
==0.00100 M
(50.00 mL)
2. Calculate A[I2]. From the indicator reaction equation, the concentration of S203 is
twice as great as the concentration of I2 produced in the time At. Therefore, the
concentration of I2 produced in time At will be one-half the concentration of S2O3
initially present in the reaction solution.
[S2O,?] = 1.00 x 10³ M; therefore A[L] = 5.00 x 10“ M
3. Normalize and then fill four burets: one with 0.200 M KI, one with 0.200 M KCI, one
with 0.100 M K2S2O8 and the remaining one with 0.100 M Na2SO4.
dependent on temp
k
At
Rate (A[I2]/At)
Run
°L*O*s]
[1] V
[I]
Units:
41.0s
0.0400 m
h-01x 00
100m
0.0400 m
3.
8 2.0s
4.
M 00100 0
(0.200 m)(20,0mL) (0.100m)(20.00 ml (o.050oml19:00 mil l All,] 2[$,0,],
00,
1. Determine the order with respect to [I].
2. Determine the order with respect to [S2Og ].](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fb234898a-ca00-4740-ae3d-79576f672843%2F4b252876-934c-4bb6-86fa-e50ad34a7519%2Fquerjmm.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
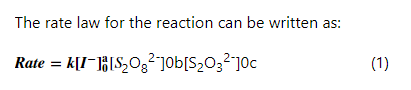
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 6 images









