how to treat type 2 diabetes?
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Accounting for 90 to 95% of those with diabetes type 2 diabetes is the most common form of the condition type 2 diabetes mellitus .It is also called non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(NIDDM) . In this type, some insulin is still made by the pancreas but in inadequate amounts . As a result there is insufficient level of insulin to control the blood sugar level. Most people with type 2 diabetes suffer from insulin resistance.Insulin resistance refers to the decrease sensitivity of tissue to the insulin. During such a condition body mistakes that there is a lack of insulin , so tries to secret more and more insulin . Gradually the higher demand of insulin not made and pancreas struggle to produce more insulin and resulting in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
There are five components of type 2 diabetes management-
1. Nutritional Management
2. Exercise to lower blood glucose
3.Pharmacological therapy
4.Blood glucose monitoring
5.Education of diabetes
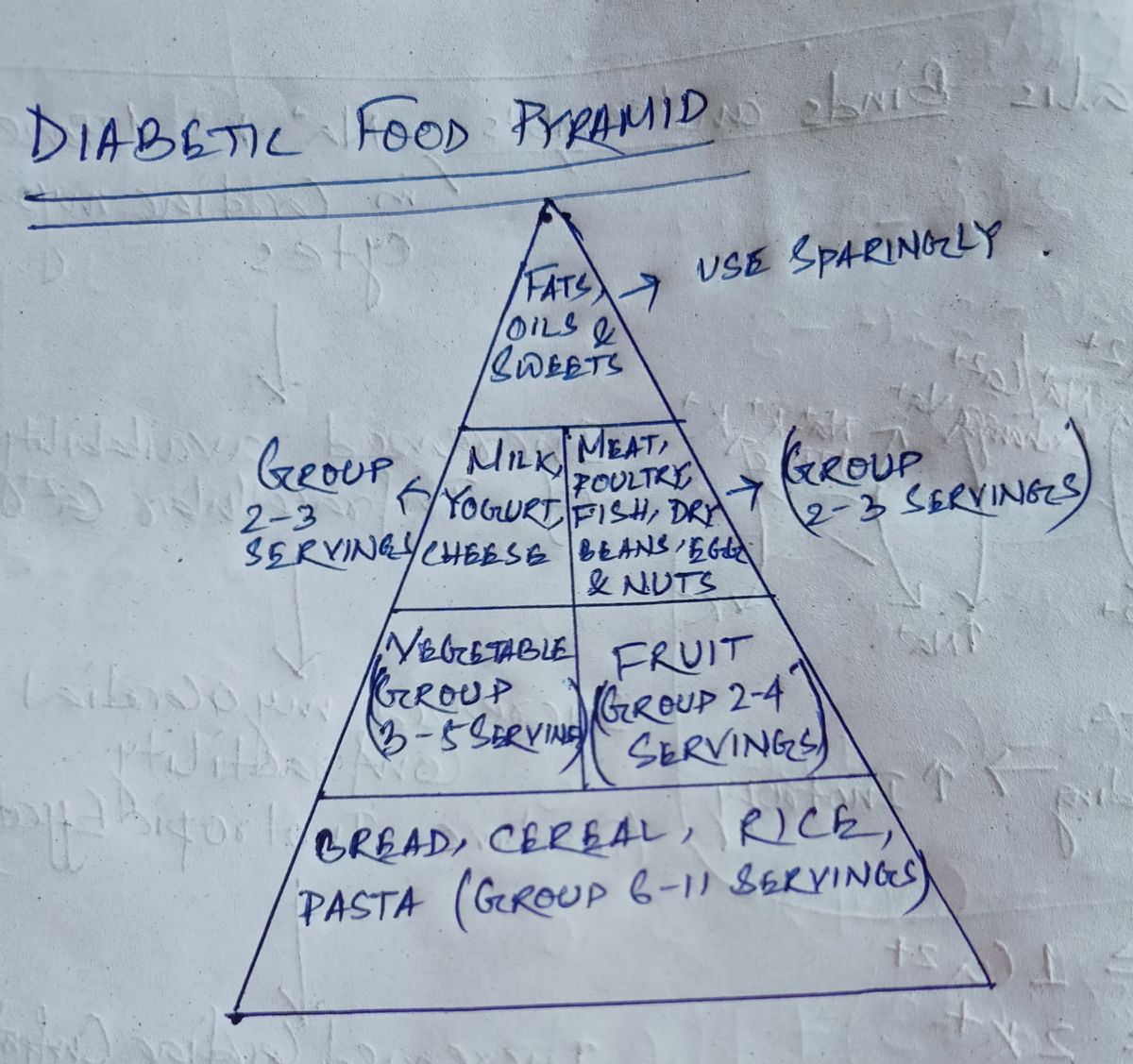
1.Nutritional Management: The dietary requirement for type 2 diabetes mellitus are critical . Type 2 diabetes diet is important to manage the blood glucose level as well as weight control. Modifying eating habits are typically important step toward the reducing blood sugar levels. Diet plays a vital role in controlling diabetes and diabetic diet is framed on the basis of height , weight and other disease and age of the individual.
- Avoid junk food as it contain lots of fat building materials and sugar content in such food is always high.
- Increased intake of low glycemic foods such foods include fruits such as apple, oranges and pears ; grains like oatmeal , Barley, peanuts and vegetables such as broccoli, green leafy vegetables , beans and peas.
- Balance diet low in fat carbohydrates and cholesterol is ideal for diabetes. For required carbohydrate intake diabetic patient can depend on food like chicken, Turkey and sea foods which are low in starch.
- high glycemic foods should be avoided like potatoes, pasta and white bread.
- salad are a good way to get required vitamins.
- Try eating 4 to 5 small meal a day than three large meal.
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
2. Exercise to lower the blood glucose level:exercise is important in helping with weight control as well as helping any medication or insulin therapy to work more efficiently. There are four kinds of activity can help diabetic patient. Patient can-
- Be extra active everyday: patient mast walk around while talk on the phone, take the dog for a walk ,walk in the garden or rake leaves ,clean the house , wash the car and take the stairs instead of elevator.
- Do aerobic exercise:doing aerobic exercise for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week provides many benefits. Patient can try walking , climbing stairs, swimming or taking a water aerobic class, dancing, riding a bicycle ,playing basketball ,volleyball etc.
- Do strength training: doing exercise with hand weights elastic band or weight machine 3 times a week build muscles .
- Stretch : stretching increase flexibility lower stress and help prevent muscle soreness.
3.A. Pharmacological therapy: Everyone with type 2 diabetes mellitus must take insulin everyday to maintain safe insulin levels or replace what their pancreas is unable to produce. Insulin is usually given in two or three injections per day generally around mil X to control the blood glucose level. If taken by mouth insulin would be destroyed in stomach before it could get into the blood where it is needed.
The required dose is determined by the level of glucose in the blood so accurate monitoring of blood glucose level is essential. It is very important to eat if the patient has taken insulin to avoid the hypoglycemia, as the insulin will lower the blood glucose level. This is called insulin reaction.
- Rapid acting insulin: Rapid acting insulin has an onset of 10-15 minutes, duration of action is 3 hours and a peak action of 1 to 2 hour after injection. Example of rapid acting insulin are insulin lispro,insulin aspart and insulin glulisine etc.
- long acting insulin: Long acting insulin has a onset of action 6to 8 hours, peak action of 12 to 16 hours and duration of action is 20 to 30 hours . Examples of long acting insulin are insulin glargine , protamine zinc insulin and insulin ultralente etc.
- short acting insulin: short acting insulin has an onset of 30 minutes to 1 hour, peak action of 2 to 3 hours and duration of action is 4 to 6 hour . Examples of short acting insulin are regular insulin(humulin R) and insulin zinc (lente) etc .
Route of injection: Subcutaneous
3.B.Oral antidiabetic agent:
People with type 2 diabetes mellitus first prescribed medication , taken in a pill form . If blood glucose levels are not controlled with oral hypoglycemic agent insulin may be necessary for the person with type 2 diabetes. There are many different types of oral antidiabetic agents , these are:
- Sulfonylurea drugs: These drugs given half an hour before food. Duration of action of these drugs is 6to 24 hours. The examples a are Tolbutamide, glibenclamide, gliclazide , glipizide and glimepiride etc.
- Biguanides: The duration of action of biguanides is 8 to 12 hours. The dose is 500 mg TDS given with food (maximum dose is 2.5 gram per day). The example is Metformin (diamet).
- Meglitinide analogue: Duration of action is 3 hours. Daily dose is 0.25-4 mg into two divided doses, given 15 minutes before breakfast and dinner. Example is Repaglinide(repa)
- D-phenylalanine derivative: duration of vaccine is 2 hours daily dose is 60- 120 mg TDS given just before food. Example is Nateglinide (natelide)
- Thiazolidinediones: duration of action is half to 24 hours. Daily dose 15 to 45 mg .The example is pioglitazone (P-Glitz).
- Alpha-Glucoside inhibitor: duration of action is 4 hours .Daily dose is 50 mg BD, gradually increase 100 mg TDS with food. The example is acarbose.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









