Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways allude to the arrangement of chemical catalyzed reactions that lead to the transformation of a substance into the final product. Metabolic pathways incorporate a progression of reaction where the substrate is changed continuously and the transitional metabolites are persistently recovered.
Glucogenesis
Glucogenesis is a metabolic pathway in which glucose is produced from carbon substrates that are not carbohydrates. This process is observed in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria and other micro organisms. The general definition for glucogenesis or gluconeogenesis is as follows,
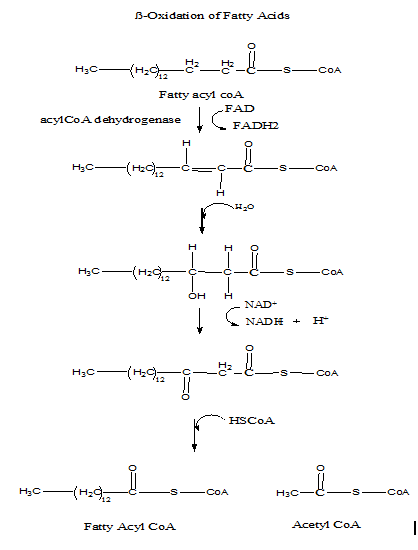
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA are obtained from the b-oxidation of one molecule of a 16-carbon saturated fatty acyl-CoA?
Introduction:
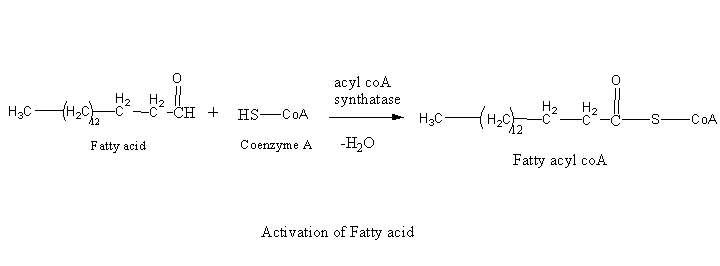
The usable energy is released in the digestion of fatty acid it is initiated on the outer mitochondrial membrane. In the digestion process first, the fatty acid is activated by fatty acyl-coenzyme. For each molecule of fatty acid activation, one molecule of coenzyme A and one molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are used.
Activation of Fatty acid:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









