How does a monopolist identify its profit-maximizing quantity of output? Then how does it decide what price to charge?
A market is a place where the sellers and the buyers interact with each other and the exchange of goods and services takes place between them at a mutually agreed price level. There are mainly two types of markets which are perfectly competitive market and imperfectly competitive market. Monopoly is the main form of the imperfect market which is characterized by the presence of the single producer and the single producer having the complete market power to determine the price and output.
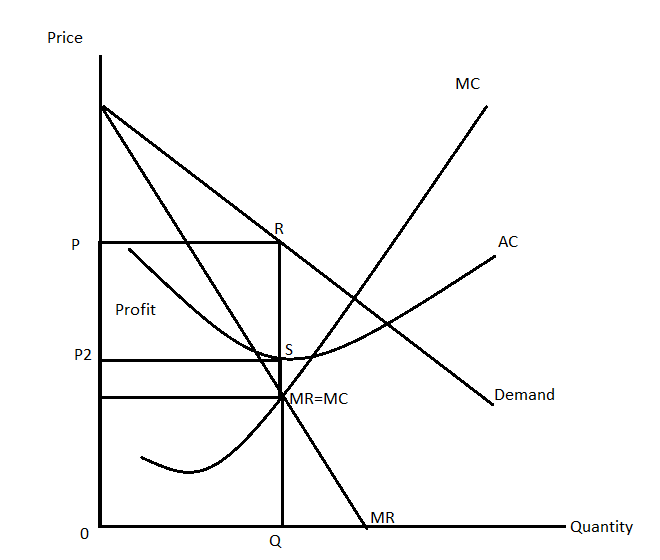
Profit maximization is the main objective of the monopolist. The monopolist identifies the profit-maximizing level of output at the point where the marginal revenue equals the marginal cost. Thus, the profit-maximizing level of output of the monopolist will be obtained at the point where the MR equals MC for the monopolist. The monopolist would extend the line from this profit-maximizing level of output up to the demand curve to identify the price which maximizes the profit for the seller. This can be illustrated as follows:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









