Why is the
Meaning of Monopolistic Competition:
The term monopolistic competition refers to the situation under which there large number of producers and a normally large number of consumers but the number remains less as compared to perfect competition.
Thus under monopolistic competition, there are close substitutes, thus a slight increase in product prices shifts the consumers to other sellers. Thus to retain their consumers the monopolistic seller, sells their products at product differentiation, so that the profit margin can be earned.
Determination of Price and Output under Monopolistic Competition:
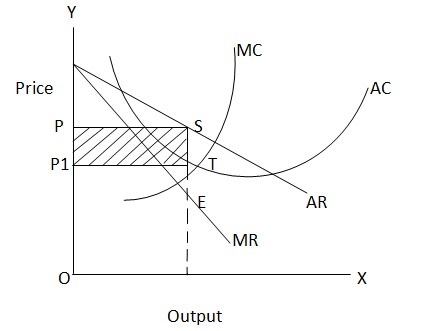
To determine the equilibrium price and output and why the monopolistic sets their prices above the marginal revenue can be determined through a diagram, which is as follows:
- Short-Run Equilibrium under Monopolistic Competition:
Under monopolistic competition, the profit can be estimated at the level where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, thus it is shown below:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









