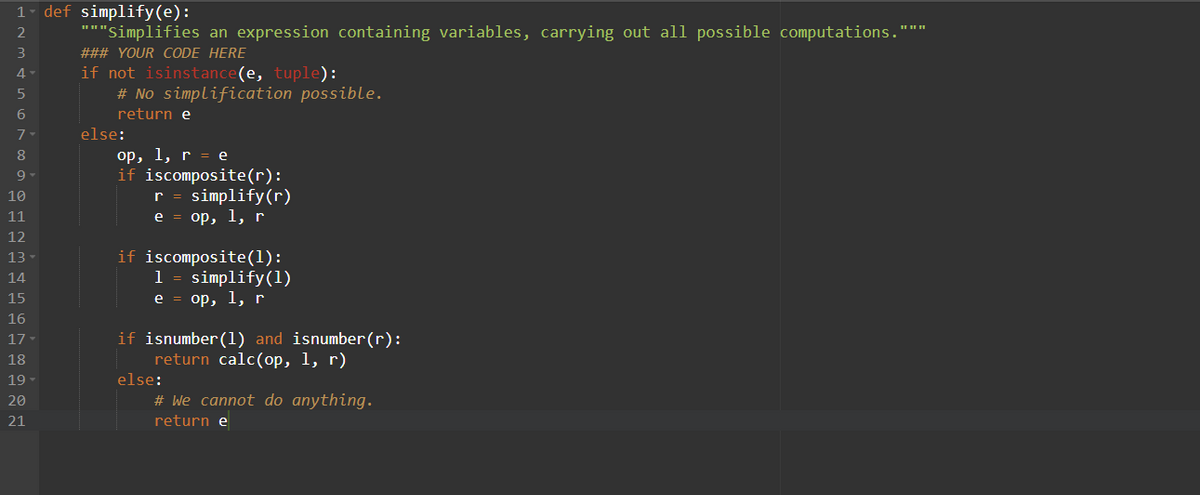
he function simplify above can perform all numerical computations, but stops whenever it encounters a variable. It cannot do any better, in fact, because it does not know the values of variables. If we specify values for variables, we can then use those values in the computation, replacing each variable whose value is specified with the value itself.
Question 1: Evaluating expressions with respect to a variable valuation.
The function simplify above can perform all numerical computations, but stops whenever it encounters a variable. It cannot do any better, in fact, because it does not know the values of variables.
If we specify values for variables, we can then use those values in the computation, replacing each variable whose value is specified with the value itself.
A variable valuation is a mapping from variables to their values; we can represent it simply as a dictionary associating to each variable a number:
You can extend the evaluation function to take as input a variable valuation. The idea is that, when you find a variable, you try to see whether its value is specified in the variable valuation. If it is, you can replace the variable with the value, and carry on. If it is not, you leave the variable as it is, since you cannot evaluate it.
To check if a variable (a string) s is in a dictionary d, you can test
s in d
and to get the value, in case it is present, you can just do d[s] of course.
WRITE CODE IN PYTHON FOR:
![[8] def simplify(e):
if isinstance(e, tuple):
op, l, r = e
# We simplify the children expressions.
11 = simplify( Add text cell
simplify(r)
rr =
# We compute the expression if we can.
if isnumber(ll) and isnumber(rr) :
return calc(op, ll, rr)
else:
return (op, l1, rr)
else:
# Leaf. No simplification is possible.
return e](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fecf10a40-9173-4876-b1dc-0585f27b87b2%2F2897d914-044b-46be-852c-4b37ce167d4c%2Fkwb3li8_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
![[2]
Os
class IllegalOperator(Exception):
pass
Let us define a helper function calc,which takes as argument an operator and two numbers, and computes the required operation. It will make
it easier to write the rest of the code.
def calc(op, left, right):
if op == "+":
return left + right
elif op ==
"_":
return left -
right
elif op ==
"*":
return left * right
elif op == "/":
return left / right
else:
raise IllegalOperator(op)
With this, we can write our compute method as follows.
[ 4] def compute(e):
if isinstance(e, tuple):
# We have an expression.
op, 1, r = e
# We compute the subexpressions.
1l = compute(1)
rr = compute(r)
# And on the basis of those, the whole expression.
return calc (op, 11, rr)
else:
# base expression; just return the number.
return e](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fecf10a40-9173-4876-b1dc-0585f27b87b2%2F2897d914-044b-46be-852c-4b37ce167d4c%2Fuqoa53r_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









