Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:Robert F. Blitzer
ChapterP: Prerequisites: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MCCP: In Exercises 1-25, simplify the given expression or perform the indicated operation (and simplify,...
Related questions
Question
The image provided below will help.

Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding Linear and Quadratic Equations through Differences**
1. **Linear Equations**:
- **Definition**: When the first differences are the same, it indicates a linear equation.
- **Characteristics**:
- The first differences are equal to the slope, \(m\).
- **General Equation**: \(f(x) = mx + b\).
2. **Quadratic Equations**:
- **Definition**: When the second differences are the same, it indicates a quadratic equation.
- **Characteristics**:
- Second differences are equal to \(2a\).
- **Finding "a"**: Divide the second differences by 2.
- **General Equation**: \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\).
- **Intercept**: \(c\) is the y-intercept.
These principles allow for the identification and formulation of equations based on the patterns in their differences.
![**Identifying the Y-Intercept from a Data Table**
In the following table, we have pairs of X and Y values. Our task is to identify the y-intercept and explain the process.
| X | Y |
|---|----|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | -3 |
| 3 | -8 |
| 4 | -13|
**Explanation:**
The y-intercept is the point where a line crosses the Y-axis, which occurs when X = 0. The given table does not provide a Y value for X = 0, so we need the equation of the line to find the y-intercept.
1. **Determine the Equation of the Line:**
- First, calculate the slope (m) using the formula:
\[
m = \frac{Y_2 - Y_1}{X_2 - X_1}
\]
Using points (1, 2) and (2, -3):
\[
m = \frac{-3 - 2}{2 - 1} = \frac{-5}{1} = -5
\]
2. **Using the Slope-Intercept Form:**
- The slope-intercept form of a line is:
\[
Y = mX + b
\]
Using point (1, 2) and slope -5:
\[
2 = -5(1) + b
\]
\[
2 = -5 + b \implies b = 7
\]
3. **Conclusion:**
- The y-intercept (b) is 7. Thus, the line crosses the Y-axis at (0, 7).
Understanding how to derive the equation from the table and find the y-intercept helps in comprehending linear relationships and graph interpretation.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe0228723-8b7c-4bd5-a03d-f7c714ce5bf0%2F65517654-a08e-4581-a749-8d092134cc23%2Fet4rzmt_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
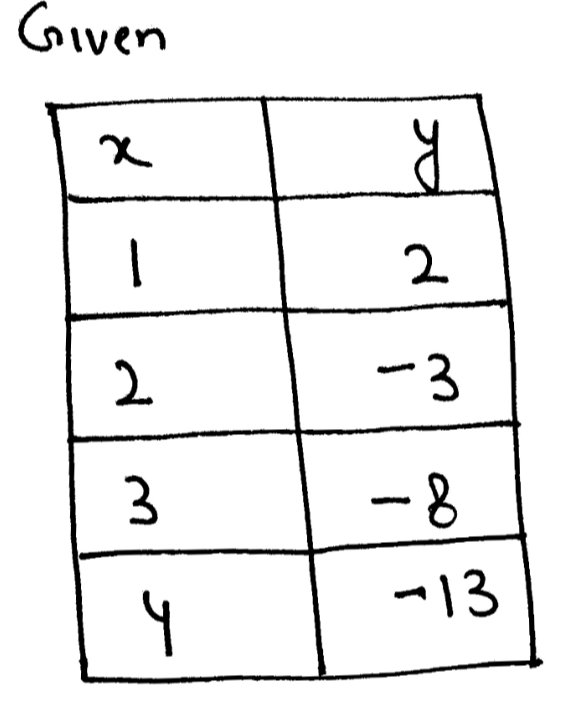
Transcribed Image Text:**Identifying the Y-Intercept from a Data Table**
In the following table, we have pairs of X and Y values. Our task is to identify the y-intercept and explain the process.
| X | Y |
|---|----|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | -3 |
| 3 | -8 |
| 4 | -13|
**Explanation:**
The y-intercept is the point where a line crosses the Y-axis, which occurs when X = 0. The given table does not provide a Y value for X = 0, so we need the equation of the line to find the y-intercept.
1. **Determine the Equation of the Line:**
- First, calculate the slope (m) using the formula:
\[
m = \frac{Y_2 - Y_1}{X_2 - X_1}
\]
Using points (1, 2) and (2, -3):
\[
m = \frac{-3 - 2}{2 - 1} = \frac{-5}{1} = -5
\]
2. **Using the Slope-Intercept Form:**
- The slope-intercept form of a line is:
\[
Y = mX + b
\]
Using point (1, 2) and slope -5:
\[
2 = -5(1) + b
\]
\[
2 = -5 + b \implies b = 7
\]
3. **Conclusion:**
- The y-intercept (b) is 7. Thus, the line crosses the Y-axis at (0, 7).
Understanding how to derive the equation from the table and find the y-intercept helps in comprehending linear relationships and graph interpretation.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780135163078
Author:
Michael Sullivan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:
9780980232776
Author:
Gilbert Strang
Publisher:
Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780077836344
Author:
Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education