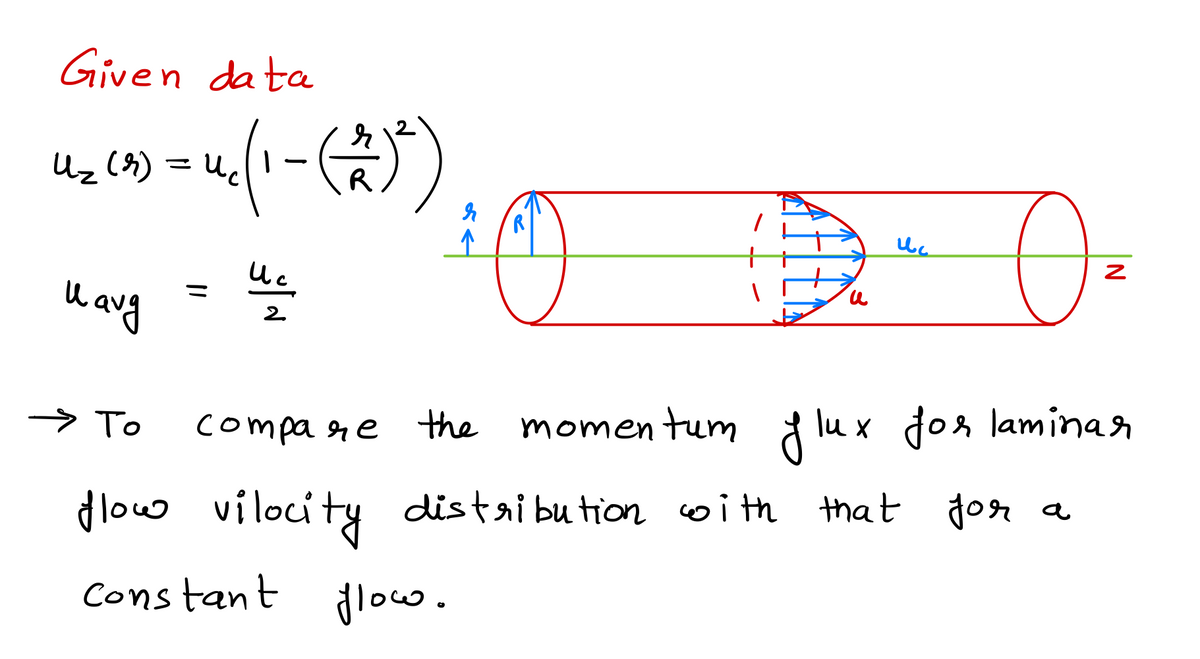
For fully-developed laminar flow through a pipe with ra- dius R, the fluid velocity is very accurately modeled as V = (Ur, Ug, U₂) = (0,0,u₂), with the axial component of velocity given by U₂ (r) = Uc = uc [1 − (7)²], - MF "c where ue is the fluid speed at the center of the pipe, r = 0. Compare the momentum flux for the laminar flow velocity distribution, uz (r), with that for a uniform How having (constant) speed uave = Uc/2, recalling that the momentum flux through a control surface is given by pV (V - ñ) dA. Ө Answer: |MF|lam = |MF|ave
For fully-developed laminar flow through a pipe with ra- dius R, the fluid velocity is very accurately modeled as V = (Ur, Ug, U₂) = (0,0,u₂), with the axial component of velocity given by U₂ (r) = Uc = uc [1 − (7)²], - MF "c where ue is the fluid speed at the center of the pipe, r = 0. Compare the momentum flux for the laminar flow velocity distribution, uz (r), with that for a uniform How having (constant) speed uave = Uc/2, recalling that the momentum flux through a control surface is given by pV (V - ñ) dA. Ө Answer: |MF|lam = |MF|ave
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
100%
![For fully-developed laminar flow through a pipe with ra-
dius R, the fluid velocity is very accurately modeled as
V = (Ur, Up, U₂) = (0,0, uz), with the axial component of
velocity given by
Ө
where ue is the fluid speed at the center of the pipe, r = 0).
Compare the momentum flux for the laminar flow velocity distribution, uz (r), with that for a uniform
flow having (constant) speed uave = uc/2, recalling that the momentum flux through a control surface
is given by
U₂(7) = uc [1 − (77)²],
z
MF
√ PV (V - ñ) dA.
Answer: |MF|lam = |MF|ave](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fab6b79a9-c663-4f87-993a-883a678be91b%2F4a1134b1-c6ba-48d8-b03c-92094398ed1a%2Ffddt449_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:For fully-developed laminar flow through a pipe with ra-
dius R, the fluid velocity is very accurately modeled as
V = (Ur, Up, U₂) = (0,0, uz), with the axial component of
velocity given by
Ө
where ue is the fluid speed at the center of the pipe, r = 0).
Compare the momentum flux for the laminar flow velocity distribution, uz (r), with that for a uniform
flow having (constant) speed uave = uc/2, recalling that the momentum flux through a control surface
is given by
U₂(7) = uc [1 − (77)²],
z
MF
√ PV (V - ñ) dA.
Answer: |MF|lam = |MF|ave
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY