Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
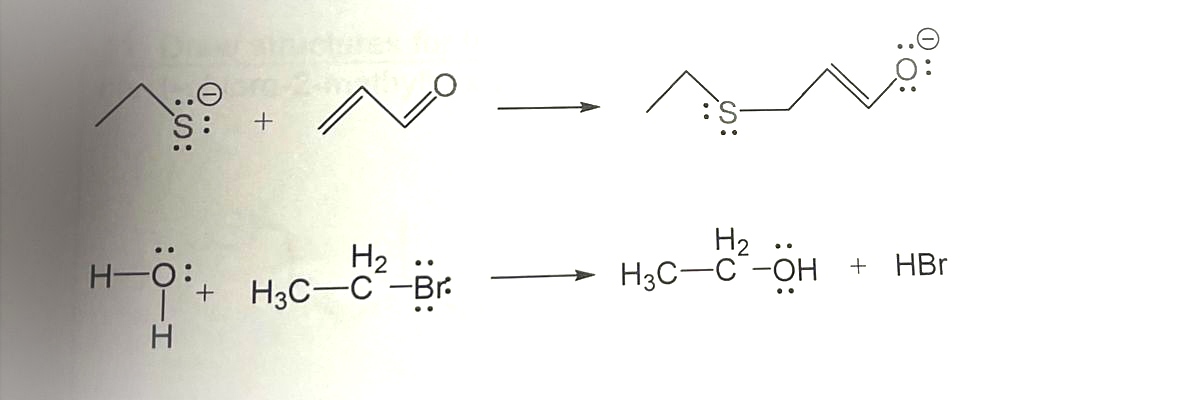
For each reaction, label the Lewis Acid and the Lewis Base
![**Transcription for Educational Website**
---
### Reaction Schemes with Sulfur and Oxygen Compounds
#### First Reaction:
- **Reactants:**
- A sulfide ion depicted as \[:S^-\], with lone pairs of electrons around the sulfur.
- An unsaturated carbonyl compound consisting of a carbon-carbon double bond (alkene) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O) with non-bonding electron pairs on the oxygen.
- **Product:**
- The resulting compound consists of the sulfur atom now bonded to one of the carbon atoms in the alkene, while the carbonyl group remains intact, displaying lone pairs on the oxygen.
The diagram clearly illustrates the movement of electrons, highlighting the attack of the sulfur's lone pair on the alkene, leading to the formation of new bonds.
#### Second Reaction:
- **Reactants:**
- A water molecule (H₂O) with lone pairs on the oxygen.
- Bromoethane (\[H₃C-CH₂-Br\]) showing a partial positive charge near the carbon atom and lone pairs on the bromine atom.
- **Products:**
- Ethanol (\[H₃C-CH₂-OH\]), with the hydroxyl group showing the lone pairs on the oxygen.
- Hydrogen bromide (HBr) as a byproduct.
This reaction depicts a classic nucleophilic substitution where the lone pair of electrons on water's oxygen attacks the electrophilic carbon in bromoethane, displacing the bromide ion and forming ethanol.
### Explanation:
Both chemical reactions demonstrate fundamental organic chemistry concepts: nucleophilic attack and substitution reactions. They serve as valuable educational examples for understanding how different functional groups interact through electron pair movements to form new chemical bonds.
---](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F3ae67fe3-740a-4982-854d-7043421396bc%2F20589143-9c03-406a-9a80-5479a7e9afa8%2Fgvaoju_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Given reaction:
Lewis acid and Lewis base are to be labelled.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images









