For a = 1.5m, determine the reactions at pin A and roller B. 1800 N/m A 4 m Solution: • There are two distributed loads acting on the beam, left and right. Replace them with equivalent concentrated loads respectively: 1. The distributed load on the left part of the beam is equivalent to F₁: o Magnitude of it: F₁ = N; o Location of it: x₁ = m to the right of A; 2. The distributed load on the right part of the beam is equivalent to F2: o Magnitude of it: F2 = N; o Location of it: X₂ = 600 N/m B 1. Reactions on A: 2 Reactions on R • The two supports are replaced by corresponding reactions: → m to the right of A;
For a = 1.5m, determine the reactions at pin A and roller B. 1800 N/m A 4 m Solution: • There are two distributed loads acting on the beam, left and right. Replace them with equivalent concentrated loads respectively: 1. The distributed load on the left part of the beam is equivalent to F₁: o Magnitude of it: F₁ = N; o Location of it: x₁ = m to the right of A; 2. The distributed load on the right part of the beam is equivalent to F2: o Magnitude of it: F2 = N; o Location of it: X₂ = 600 N/m B 1. Reactions on A: 2 Reactions on R • The two supports are replaced by corresponding reactions: → m to the right of A;
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription of the Image on Distributed Loads on a Beam:**
---
**Solution:**
There are two distributed loads acting on the beam, left and right. Replace them with equivalent concentrated loads respectively:
1. **The distributed load on the left part of the beam is equivalent to F₁:**
- Magnitude of it: F₁ = _____ N;
- Location of it: x₁ = _____ m to the right of A;
2. **The distributed load on the right part of the beam is equivalent to F₂:**
- Magnitude of it: F₂ = _____ N;
- Location of it: x₂ = _____ m to the right of A;
- **The two supports are replaced by corresponding reactions:**
1. Reactions on A:
- (Dropdown)
2. Reactions on B:
- (Dropdown)
- **Equilibrium equations:**
1. ΣFₓ = 0: Aₓ = _____;
2. ΣMₐ = 0: Bᵧ = _____ N;
3. ΣMᵦ = 0: Aᵧ = _____ N;
---
**Explanation:**
The document outlines a problem involving two distributed loads on a beam. The goal is to replace these distributed loads with equivalent concentrated loads at specific locations. There are placeholders for students to input the magnitude and location of these forces. Additionally, it involves calculating the reactions at two supports, A and B, and determining the equilibrium conditions with given equations. Students are expected to engage with dropdown menus and fill in the blanks with the appropriate values.

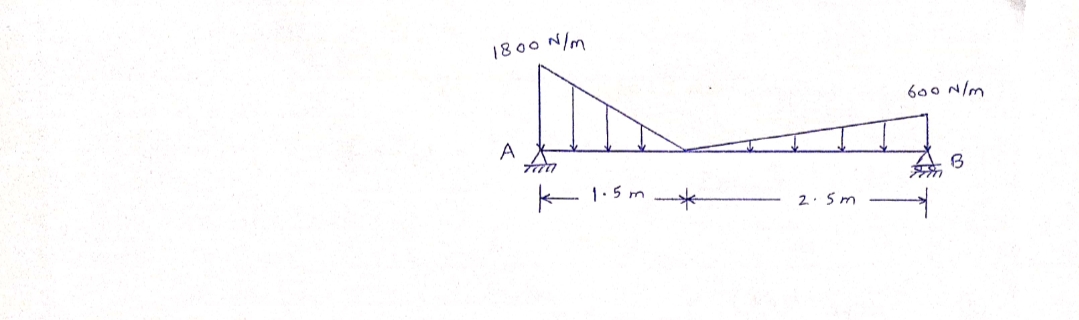
Transcribed Image Text:**Beam Reactions Calculation**
**Problem Statement:**
For \( a = 1.5 \, \text{m} \), determine the reactions at pin A and roller B.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The image shows a beam supported by a pin at point A on the left and a roller at point B on the right. The beam is subjected to two distributed loads: 1800 N/m on the left part and 600 N/m on the right part. The section between A and B spans 4 m.
**Solution:**
- **Distributed Loads:**
There are two distributed loads acting on the beam, divided into left and right segments. These loads are replaced by equivalent concentrated loads:
1. **Left Segment Load:**
- The distributed load on the left part of the beam is equivalent to \( F_1 \):
- Magnitude of \( F_1 \): _______ N
- Location of \( x_1 \): _______ m to the right of A
2. **Right Segment Load:**
- The distributed load on the right part of the beam is equivalent to \( F_2 \):
- Magnitude of \( F_2 \): _______ N
- Location of \( x_2 \): _______ m to the right of A
- **Support Reactions:**
The two supports will be replaced by corresponding reactions:
1. Reactions on A: _______
2. Reactions on B: _______
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning