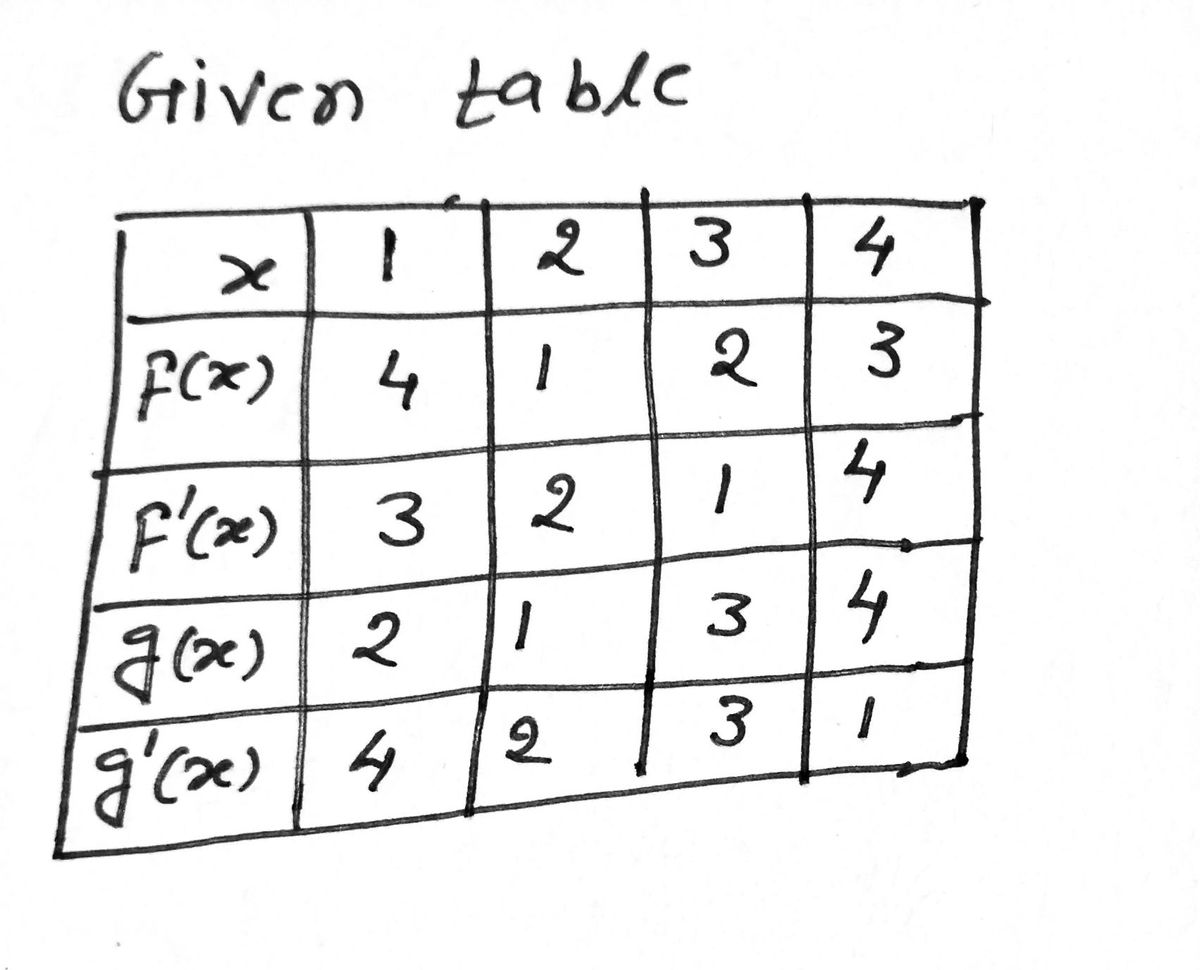
Find the following using the table below. X f(x) f'(x) 1 2 3 4 +3+ 4 g(x) 2 g'(x) 4 1 2 -~-~ -33 1 2 NW 2 3 4 4 h'(1) if h(x) = - 1 1 h'(1) if h(x) = f(x) · g(x) f(x) g(x) h'(1) if h(x) = f(g(x))
Find the following using the table below. X f(x) f'(x) 1 2 3 4 +3+ 4 g(x) 2 g'(x) 4 1 2 -~-~ -33 1 2 NW 2 3 4 4 h'(1) if h(x) = - 1 1 h'(1) if h(x) = f(x) · g(x) f(x) g(x) h'(1) if h(x) = f(g(x))
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:### Instructions:
Use the given table to solve the following problems.
#### Table of Values:
The table contains values for functions \( f(x) \), \( f'(x) \), \( g(x) \), and \( g'(x) \) at specific points \( x \).
| \( x \) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|----------|---|---|---|---|
| \( f(x) \) | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| \( f'(x) \) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| \( g(x) \) | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| \( g'(x) \) | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
#### Problems to Solve:
1. **Calculate** \( h'(1) \) **if** \( h(x) = f(x) \cdot g(x) \).
2. **Calculate** \( h'(1) \) **if** \( h(x) = \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} \).
3. **Calculate** \( h'(1) \) **if** \( h(x) = f(g(x)) \).
#### Explanation of Solutions:
For each problem, apply appropriate differentiation rules:
- **Product Rule** for \( h(x) = f(x) \cdot g(x) \).
- **Quotient Rule** for \( h(x) = \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} \).
- **Chain Rule** for \( h(x) = f(g(x)) \).
Use the values from the table to substitute and find the derivatives at \( x = 1 \). Fill in your solutions in the spaces provided.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning