Find the centroid point of the area below given that a = 12 in. a a Solution: • The composite area can be divided into 3 basic shapes, called rectangular, triangle and semi-circle; Triangle Component Dimensions_(in) A, (in²) Rectangular = Semicircle h = b= a h= 2a r= ΣΑ = , in y, in XA, in ³ Σ = A, in3 Σ=
Find the centroid point of the area below given that a = 12 in. a a Solution: • The composite area can be divided into 3 basic shapes, called rectangular, triangle and semi-circle; Triangle Component Dimensions_(in) A, (in²) Rectangular = Semicircle h = b= a h= 2a r= ΣΑ = , in y, in XA, in ³ Σ = A, in3 Σ=
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![This image contains a table used for calculating the centroids and areas for different geometric shapes. It seems to be an educational tool for understanding moments of area and centroid locations.
### Table Structure:
#### Columns:
1. **Component**: Lists the geometric shapes, including a rectangle, triangle, and semicircle.
2. **Dimensions (in)**: Specifies parameters relevant to each shape, such as base (b), height (h), and radius (r).
3. **A\[_i\], (in\[^2\])**: Denotes the area of each component.
4. **\[\overline{x}\], in**: X-coordinate of the centroid for each shape.
5. **\[\overline{y}\], in**: Y-coordinate of the centroid for each shape.
6. **\[\overline{x}A\], in\[^3\]**: Product of the x-coordinate of the centroid and the respective area.
7. **\[\overline{y}A\], in\[^3\]**: Product of the y-coordinate of the centroid and the respective area.
#### Rows:
- **Rectangular**: Dimensions are \(b\) (base) and \(h\) (height).
- **Triangle**: Dimensions are \(b\) (base) and \(h\) (height).
- **Semicircle**: Dimension is \(r\) (radius).
#### Bottom summary row includes:
- \[\Sigma A\]: Total area calculation.
- \[\Sigma\]: Total for \[\overline{x}A\].
- \[\Sigma\]: Total for \[\overline{y}A\].
### Calculations Below the Table:
- **First Moments of the Area**:
1. \(Qx = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \) in\[^3\]
2. \(Qy = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \) in\[^3\]
- **Location of Centroid**:
1. \(\overline{x} = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) in
2. \(\overline{y} = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) in
This structured layout assists students in understanding the process of calculating centroids and moments of areas which are fundamental in the study of mechanics and structural analysis.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9a42e238-4116-4e80-81a7-f4d567b4bd0e%2F27bf0369-4856-4859-95e8-82321def7f76%2Fuho1ewp_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:This image contains a table used for calculating the centroids and areas for different geometric shapes. It seems to be an educational tool for understanding moments of area and centroid locations.
### Table Structure:
#### Columns:
1. **Component**: Lists the geometric shapes, including a rectangle, triangle, and semicircle.
2. **Dimensions (in)**: Specifies parameters relevant to each shape, such as base (b), height (h), and radius (r).
3. **A\[_i\], (in\[^2\])**: Denotes the area of each component.
4. **\[\overline{x}\], in**: X-coordinate of the centroid for each shape.
5. **\[\overline{y}\], in**: Y-coordinate of the centroid for each shape.
6. **\[\overline{x}A\], in\[^3\]**: Product of the x-coordinate of the centroid and the respective area.
7. **\[\overline{y}A\], in\[^3\]**: Product of the y-coordinate of the centroid and the respective area.
#### Rows:
- **Rectangular**: Dimensions are \(b\) (base) and \(h\) (height).
- **Triangle**: Dimensions are \(b\) (base) and \(h\) (height).
- **Semicircle**: Dimension is \(r\) (radius).
#### Bottom summary row includes:
- \[\Sigma A\]: Total area calculation.
- \[\Sigma\]: Total for \[\overline{x}A\].
- \[\Sigma\]: Total for \[\overline{y}A\].
### Calculations Below the Table:
- **First Moments of the Area**:
1. \(Qx = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \) in\[^3\]
2. \(Qy = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \) in\[^3\]
- **Location of Centroid**:
1. \(\overline{x} = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) in
2. \(\overline{y} = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) in
This structured layout assists students in understanding the process of calculating centroids and moments of areas which are fundamental in the study of mechanics and structural analysis.
![**Find the centroid point of the area below given that \(a = 12\) in.**
[Diagram Explanation]: The diagram shows a composite shape on a coordinate plane with three sub-shapes: a rectangle, a triangle, and a semicircle. The rectangle has dimensions \(a\) by \(a\), with a triangle on top having a base of \(a\) and height \(a\). The semicircle, which is located next to the rectangle, has a diameter of \(2a\).
**Solution:**
- The composite area can be divided into 3 basic shapes: rectangle, triangle, and semicircle.
| Component | Dimensions (in) | \(A, \, (\text{in}^2)\) | \(\bar{x}, \, \text{in}\) | \(\bar{y}, \, \text{in}\) | \(\bar{x}A, \, \text{in}^3\) | \(\bar{y}A, \, \text{in}^3\) |
|-------------|-----------------|--------------------|----------------|----------------|----------------------------|----------------------------|
| Rectangle | \(b = \) | | | | | |
| | \(h = \) | | | | | |
| Triangle | \(b = \) | | | | | |
| | \(h = \) | | | | | |
| Semicircle | \(r = \) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | \(\Sigma A =\) | | | | \(\Sigma =\) | \(\Sigma =\) |
- The table outlines areas (\(A\)), centroid coordinates (\(\bar{x}\), \(\bar{y}\)), and the moments (\(\bar{x}A\), \(\bar{y}A\)) for each shape.
The information above is formatted for use in an educational context, providing a structured breakdown for calculating the centroid of a composite shape through its subdivided components.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9a42e238-4116-4e80-81a7-f4d567b4bd0e%2F27bf0369-4856-4859-95e8-82321def7f76%2Fr8co1_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Find the centroid point of the area below given that \(a = 12\) in.**
[Diagram Explanation]: The diagram shows a composite shape on a coordinate plane with three sub-shapes: a rectangle, a triangle, and a semicircle. The rectangle has dimensions \(a\) by \(a\), with a triangle on top having a base of \(a\) and height \(a\). The semicircle, which is located next to the rectangle, has a diameter of \(2a\).
**Solution:**
- The composite area can be divided into 3 basic shapes: rectangle, triangle, and semicircle.
| Component | Dimensions (in) | \(A, \, (\text{in}^2)\) | \(\bar{x}, \, \text{in}\) | \(\bar{y}, \, \text{in}\) | \(\bar{x}A, \, \text{in}^3\) | \(\bar{y}A, \, \text{in}^3\) |
|-------------|-----------------|--------------------|----------------|----------------|----------------------------|----------------------------|
| Rectangle | \(b = \) | | | | | |
| | \(h = \) | | | | | |
| Triangle | \(b = \) | | | | | |
| | \(h = \) | | | | | |
| Semicircle | \(r = \) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | \(\Sigma A =\) | | | | \(\Sigma =\) | \(\Sigma =\) |
- The table outlines areas (\(A\)), centroid coordinates (\(\bar{x}\), \(\bar{y}\)), and the moments (\(\bar{x}A\), \(\bar{y}A\)) for each shape.
The information above is formatted for use in an educational context, providing a structured breakdown for calculating the centroid of a composite shape through its subdivided components.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given data:-
The given value of a is 12 in.
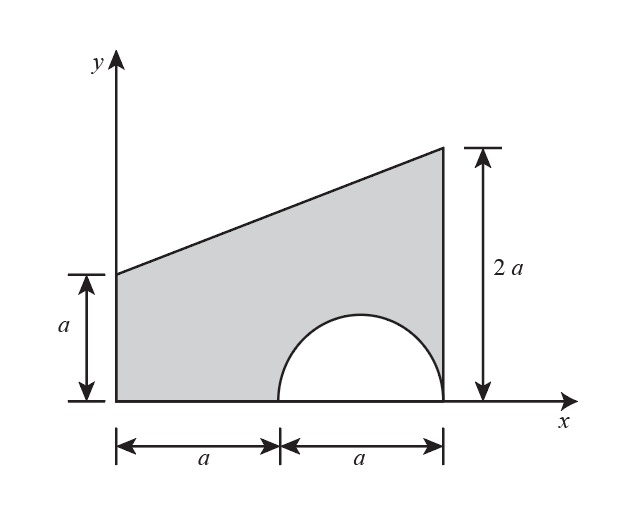
After cutting the section,
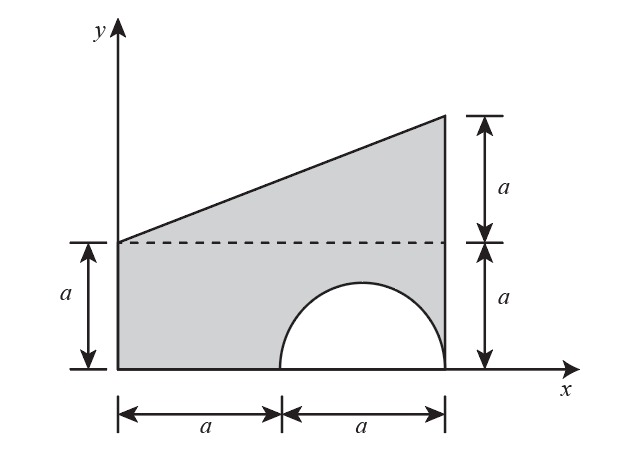
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning