College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
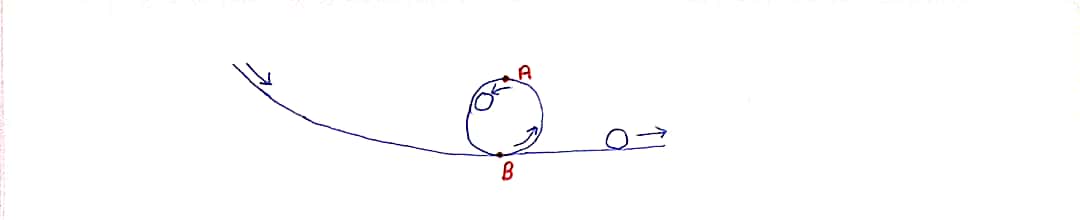
Observe the motion of a ball that rolls down a track and then executes a loop-the-loop, provided it has sufficient velocity. Draw and label the forces in a free body diagram for the ball when it is at the top and at the bottom of the loop.

Transcribed Image Text:### Transcription and Explanation for Educational Purposes
**Figure 7-12: Motion of a Ball in a Loop**
This diagram illustrates the path of a ball as it moves through a loop. It is divided into different sections showing the trajectory and forces acting on the ball at various points along its path.
1. **Initial Descent and Entry:**
- The ball begins its motion from a higher point on the left side of the diagram and moves downward along a curved path due to gravitational force.
- An arrow indicates the direction of motion as the ball enters the loop.
2. **Inside the Loop:**
- As the ball moves inside the circular loop, arrows illustrate both its direction and the centripetal force acting towards the center of the loop.
- This is crucial for maintaining circular motion.
3. **Forces at Different Points:**
- **FBD (Free Body Diagram):** Represents the different forces acting on the ball at a point inside the loop.
- **TOP:** At the top of the loop, the direction of the motion is horizontal, shown by a rightward arrow. The forces at this point include gravitational force downward and centripetal force towards the center of the circle.
- **BOTTOM:** At the bottom of the loop, the speed is highest, and the direction is horizontal as the ball exits the loop, shown by another rightward arrow.
By understanding the forces and motion path, one can analyze the dynamics of circular motion, including aspects such as speed, gravitational forces, and the role of centripetal acceleration. This diagram serves as a visualization tool to explain these physical concepts effectively.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON