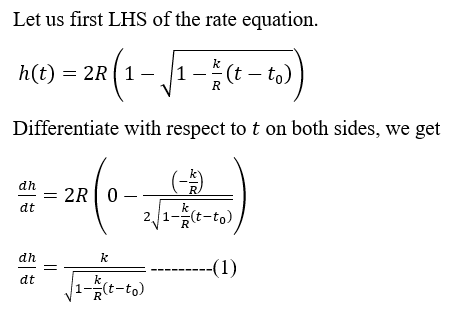
(f) Show that the function h (t) = 2R (1– /1-(t – to)) satisfies the related rate equation that you wrote in (b). Pick values k = -0.3, to = 1, 2, 3, 4, R = 1 and produce four graphs of this function.
Unitary Method
The word “unitary” comes from the word “unit”, which means a single and complete entity. In this method, we find the value of a unit product from the given number of products, and then we solve for the other number of products.
Speed, Time, and Distance
Imagine you and 3 of your friends are planning to go to the playground at 6 in the evening. Your house is one mile away from the playground and one of your friends named Jim must start at 5 pm to reach the playground by walk. The other two friends are 3 miles away.
Profit and Loss
The amount earned or lost on the sale of one or more items is referred to as the profit or loss on that item.
Units and Measurements
Measurements and comparisons are the foundation of science and engineering. We, therefore, need rules that tell us how things are measured and compared. For these measurements and comparisons, we perform certain experiments, and we will need the experiments to set up the devices.
First image is the word problem context. Please answer PART F from second image. Please show all steps and explain with clear handwriting. No cursive if possible.
![**GUIDED INSTRUCTION**
**(a)** Express the assumption that "the rate of change of the volume of water, \( V \), is proportional to the surface area \( A \)."
Use a proportionality constant \( k \) (which may be named as "porosity"). Is it a positive or a negative constant? Since this is a crucial step, I will just write the answer for you.
\[ \frac{dV}{dt} = kA \]
**(b)** Use the given formulas for the volume and area (displayed above the diagram) to rewrite the equation in (a) as an equation for \( h \) and \( \frac{dh}{dt} \). (We will call this a related rate equation.)
**(c)** Solve the related rate equation from (b) for \( \frac{dh}{dt} \) and simplify it. Use this equation to explain why the drain rate \( h' (t) \) cannot be a constant function unless the filter is completely clogged (that is, unless \( k = 0 \)). [Hint: You may use \( h'' (t) \) to be able to answer this. There are other ways, too.] Suppose the water is completely drained at a time \( t = t_0 \). Talk about the limits \( \lim_{t \to t_0 ^-} [h (t)] \) and \( \lim_{t \to t_0 ^-} [h' (t)] \). To answer these, make an assumption that \( h (t) \) is a monotonically decreasing continuous function (i.e. water doesn't climb back up!), and that \( h (t_0) = 0 \). Verify your findings analytically by using the related rate equation.
**(d)** Study the concavity of the graph of the function \( h \). We do this so we know whether the water level goes down faster and faster or slower and slower. Is the graph of \( h \) always concave up or always concave down or does it have an inflection point? Provide a physical explanation to your finding about the concavity.
**(e)** Sketch a reasonable graph of \( h (t) \) and of \( h' (t) \) based on your answers in (c) and (d). Certain properties of the graph (such as slope at \( t_0](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F28092663-10ce-474b-a101-95a46deb92bf%2Fda1a4087-d2a7-475b-a835-8d272d7e2369%2F58qvfk.png&w=3840&q=75)
![# Problem Choice 2.1: Understanding Water Drainage in a Spherical Filter
In this problem, we will consider a filter that is shaped as a lower semi-sphere. The picture below shows a spherical filter with water filled to level \( h \). The following formulas are essential for completing this work:
- The volume of water filled to level \( h \) in a spherical bowl with radius \( R \) is given by:
\[ V = \pi h^2 \left( R - \frac{h}{3} \right) \]
- Another crucial formula is:
\[ A = 2\pi R h \]
for the surface area of the part of the sphere that is in contact with the body of water.

In the diagram, the semi-spherical filter is shown with water filled up to a height \( h \) and radius \( R \).
We will investigate the relationship between the water level (\( h \)) and the rate at which this level changes ( \(\frac{dh}{dt}\) ) based on the assumption that the drain rate (the rate at which the volume of the water decreases) is proportional to the surface area of contact. (This is approximately what happens with an actual coffee filter!) Ultimately, we are interested in expressing \( h \) as a function of time \( t \).
Please read on for more detailed instructions below.
### CONTEXT
To put your mind in a more concrete context, let's think about a cone-shaped filter. For the filter of any shape, water is drained at a rate that is proportional to the contact area. In the case of a right-angle cone filter, this area is \( \sqrt{2} \pi h^2 \). So,
\[ \frac{dV}{dt} = \sqrt{2} \pi k h^2 \]
for some negative constant \( k \). But, since \( V = \frac{1}{3} \pi h^3 \) (for a right-angle cone), we have:
\[ \sqrt{2} \pi k h^2 = \pi h^2 \cdot \frac{dh}{dt} \implies \sqrt{2}k = \frac{dh}{dt} \]
This tells us that the water level will decrease at a constant rate. In the case of a spherical funnel, will we arrive](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F28092663-10ce-474b-a101-95a46deb92bf%2Fda1a4087-d2a7-475b-a835-8d272d7e2369%2F55ox5sh.png&w=3840&q=75)
Sub question (f):
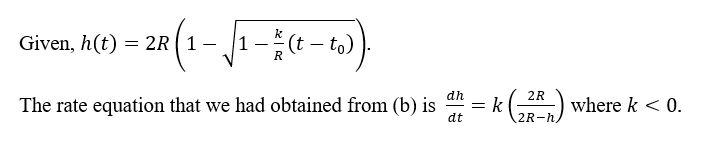
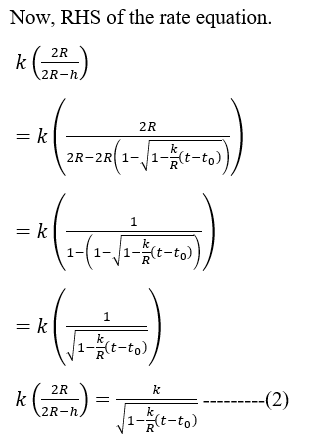
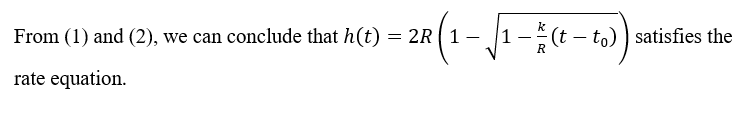
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 6 images









