explain the motion of charged particles in a uniform electric field at x and y coordinates (two dimensions)
Q: A rod carrying a total charge 14.7 µC uniformly distributed along its length 8.5 m (constant λ) and…
A:
Q: A small plastic bead has a mass of 3.94 g and a charge of -18.2 µC. It levitates, motionless, when…
A:
Q: A spherical rain drop of radius 1.00 mm has a charge speed of an identical but uncharged drop is…
A:
Q: An electron initially placed 0.50 m to the right of a small charged sphere moves to the right with…
A:
Q: Two horizontal plates of opposite charge form a constant electric field = 1000 N/C directed…
A:
Q: Two point charges, q₁ = 1.2 x 10-7 C and q₂ = -5.8 x 10-8 C, are held 35.0 cm apart. (Assume q2 is…
A: We are given 2 point charges and their separation distance. We are also given distance of point…
Q: A small object of mass 4.00 g and charge −17.3 μC is suspended motionless above the ground when…
A: Since the object is motionless, the net force on it must be zero. The forces acting on the object…
Q: electric field
A:
Q: The figure below shows a dipole. If the positive particle has a charge of 39.3 mC and the particles…
A:
Q: An electron with charge e travelling at a horizontal speed of 1.50 x 10 m s¹ enters a region of…
A: Since you have asked multiple questions, we will solve the first question for you. If you want any…
Q: Three charges are at the corners of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure below. Calculate…
A: We know that the electric field due to the positive charge is away and due to the negative charge is…
Q: Chapter 22, Problem 014 In the figure particle 1 of charge q1 = -6.28q and particle 2 of charge q2 =…
A:
Q: In figure 2, an upwardly oriented uniform electric field E⃗ of a magnitude of 2.0 × 103 N / C has…
A: (a) If the electron will hit the upper plane that means, y=d. Now the initial velocity (u) of the…
Q: nitude of the ele
A: A field is a way of conceptualizing and mapping the force that surrounds any object and acts on…
Q: Charge Q=3 nC is uniformly distributed around a conducting ring of radius 8 cm, as in the figure.…
A:
Q: A particle of charge q=10C floats in static equilibrium above a uniformly charged infinite plane. If…
A:
Q: Two particles, each with charge 52.3 nC, are located on the y axis at y = 27.5 cm and y=-27.5 cm.…
A:
Q: The electric field
A: Given:Magnitude = 704 N/CThe plate separation = 4.06 cm
Q: Suppose there are two uniformly charged non-conducting spheres, one with a charge +Q, the other of…
A: Electric field at a point can be defined as force acting on unit positive test charge kept at that…
Q: What must the charge (sign and magnitude) of a 3.45 gg particle be for it to remain stationary when…
A:
Q: Points A and B are distances 2d and 3d from a positive charge +q and lie on the same line. When a…
A: Given : 1st Charge is +q; Points A and B are distanced 2d and 3d from charge +q ; second charge is…
Q: Problem 12: A uniformly charged rod of length L = 1.4 m lies along the x-axis with its right end…
A:
Q: A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of a uniform electric field E= -3.00…
A: Explanation and solution shown in the picture below ?
Q: An electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field . The electron accelerates vertically…
A: The expression for the electric field is written as, Here, F and q represent the force on an…
Q: A uniform electric field exists in the region between two oppositely charged plane parallel plates.…
A:
Q: figure below shows (Express your answer in vector form.) E= X N/C d/2 y d/2 positive particle has a…
A:
Q: 1 nC, and 1 nC, are located along the x-axis with the positions q,(x, y) = (0, 0) and q2(x, y) = (2…
A: Consider the figure below.
Q: A charge q1=+2q is at the origin, and a charge q2=−q is on the x-axis at x=a, where a>0. Find the…
A: Given: q1=+2q at x=o q2 = -q at x=a (a>0)
Q: The figure below shows a dipole. If the positive particle has a charge of 36.9 mC and the particles…
A: Electric dipole is a combination of two equal magnitude of charges but opposite in polarity…
Q: The figure below shows a dipole. If the positive particle has a charge of 31.9 mC and the particles…
A:
Q: In this example, we will analyze the motion of an electron that is released in an electric field.…
A:
Q: The electric field at point P is 9.3 x 1020 N/C @ 343°. What is the angle of the force experienced…
A:
Q: An electron and a proton are fixed at a separation distance of 859 nm. Find the magnitude E and the…
A: Given Separation distance between electron and proton is 859 nm = 8.59x10-7 m Distance of electron…
explain the motion of charged particles in a uniform electric field at x and y coordinates (two dimensions)
Basic Details
The initial velocity of the particle along the x axis is v and along the y axis is zero. The acceleration along the axis can be determined by the force due to electric field. The motion of the particle along the axis can be determined by the second equation of motion.

Calculations
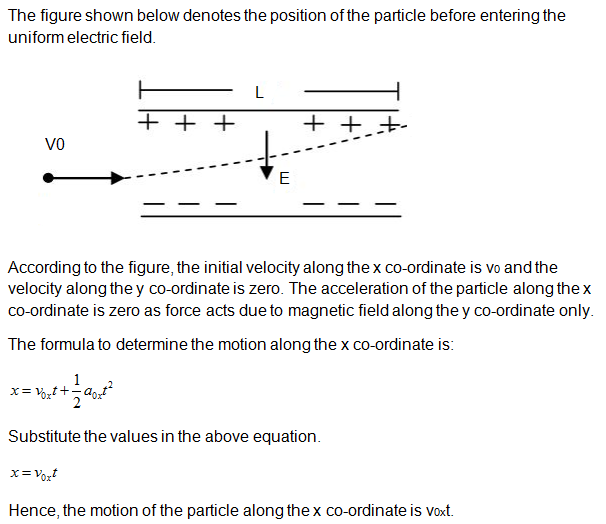
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

- A 4.1 MC point charge is placed on the x-axis at the point X₁ = -22.5m. A second, 2.7-MC point Charge is placed on the x-axis at the point X₂ = 10.3m. What is the x-component of the net electric field (in N/C) at the origin? (Remember that vector components can be positive or negative) N/C= A particle with charge 9₁ = +4.7 μC is located at (x=0,y=0). A second particle with charge 92 is located at (x=0,y=4.00 cm), and a third charge 93 = +5.4 µC is located at (x=3.00 cm,y=0). (a) In your notebook, draw a diagram of the three-charge system showing the location of the charges. (b) Calculate the potential energy of this three-charge system. PE = J -8 μCA point charge located at the origin generates an electric field that has the value E = (830 N/C) i + (150 N/C) j at the point (x, y) = (2.50 m, 3.20 m). What is the value of the charge?
- The figure below shows a charged particle, with a charge of q = +38.0 nC, that moves a distance of d = 0.185 m from point A to point B in the presence of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 245 N/C, pointing right. A positive point charge q is initially at point A, then moves a distance d to the right to point B. Electric field vector E points to the right. (a) What is the magnitude (in N) and direction of the electric force on the particle? magnitude Ndirection ---Select--- toward the right toward the left The magnitude is zero. (b) What is the work (in J) done on the particle by the electric force as it moves from A to B? J (c) What is the change of the electric potential energy (in J) as the particle moves from A to B? (The system consists of the particle and all its surroundings.) PEB − PEA = J (d) What is the potential difference (in V) between A and B? VB − VA = VA charged plastic ball of mass 5.00g is placed in a uniform electric field pointing vertically upwards with a strength of 300.0NC. Calculate the magnitude and sign of the charge required on the ball in order to create a force upwards that exactly equals the weight force of the ball.An electric dipole consists of two charges, +4 μC and -4 μC, separated by a distance of 2 cm. Determine the electric field strength at a point on the axial line of the dipole, 4 cm away from its center.
- A positively charged particle of mass 50 grams and charge 10 µC is released from rest at the origin in the uniform electric field of 100 N/C directed along the +X-axis. Determine its speed at x = 10 cm position.What must the charge (sign and magnitude) of a 2.45 g particle be for it to remain stationary when placed in a downward-directed electric field of magnitude 650 N/C ? Express your answer in microcoulombs.Two positive point charges, each 15 μC, lie along the x-axis at x = –0.15 m and x = +0.15 m. Find the electric field at (a) the origin (0,0) and (b) the point (0, 0.20 m) on the y-axis. Include a diagram.