The mechanisms shown below have been proposed to explain the kinetics of the reaction
2 NO (g) + 2 H2 (g) ⇄ N2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
Mechanism I
H2 (g) + 2 NO (g) ⇄ N2O (g) + H2O (g) (fast)
H2 (g) + N2O (g) H2O (g) + N2 (g) (slow)
Mechanism II
H2 (g) + 2 NO (g) N2O (g) + H2O (g) (slow)
H2 (g) + N2O (g) ⇄ H2O (g) + N2 (g) (fast)
Mechanism III
H2 (g) + NO (g) 2 H2O (g) + N (g) (slow)
N (g) + NO (g) ⇄ N2 (g) + O (g) (fast)
H2 (g) + O (g) H2O (g) (fast)
Which is consistent with the following experimental data?
![Experiment NOI MH2] (M)Initial rate of increase in N2] (M/s)
0.005
0.015
0.005
0.010
0.010
0.020
3.0 x 10
2.7 x 105
6.0 x 106](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F053a7dd4-6035-4ca1-b497-47ec6b123526%2F6e609cc1-8f15-4a95-940e-9ba599caaec6%2Fppsvps.png&w=3840&q=75)
The relationship between reactants and products of a reaction at equilibrium (where the concentration of products and reactants are constant) with respect to a specific unit is said to be equilibrium constant of that reaction.
The mathematical expression for equilibrium constant for a reaction is:
where A, B and C are the chemical species. a, b and c are the coefficients in the balanced chemical reaction. Square brackets represents the concentration of the chemical species.
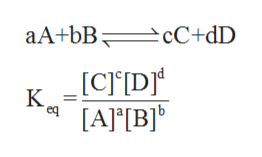
Rate is defined as the speed at which reactants is transformed into products.
An expression that states the relationship between the rate of the reaction to the rate constant and the concentrations of the reactants is known as rate law.
The given balanced chemical reaction is as follows:
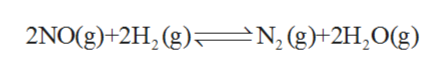
In order to determine the rate law expression of the given equation, let the rate law be given as:
where k is rate constant, x is the order of the reaction withrespect to NO and y is the order of reaction with respect to H2.
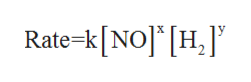
In order to determine the value of x, will take the ratio of Experiment 1 with respect to Experiment 2.
The calculation is shown below:
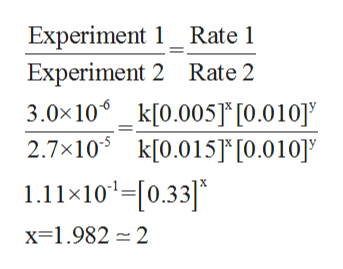
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 7 images









