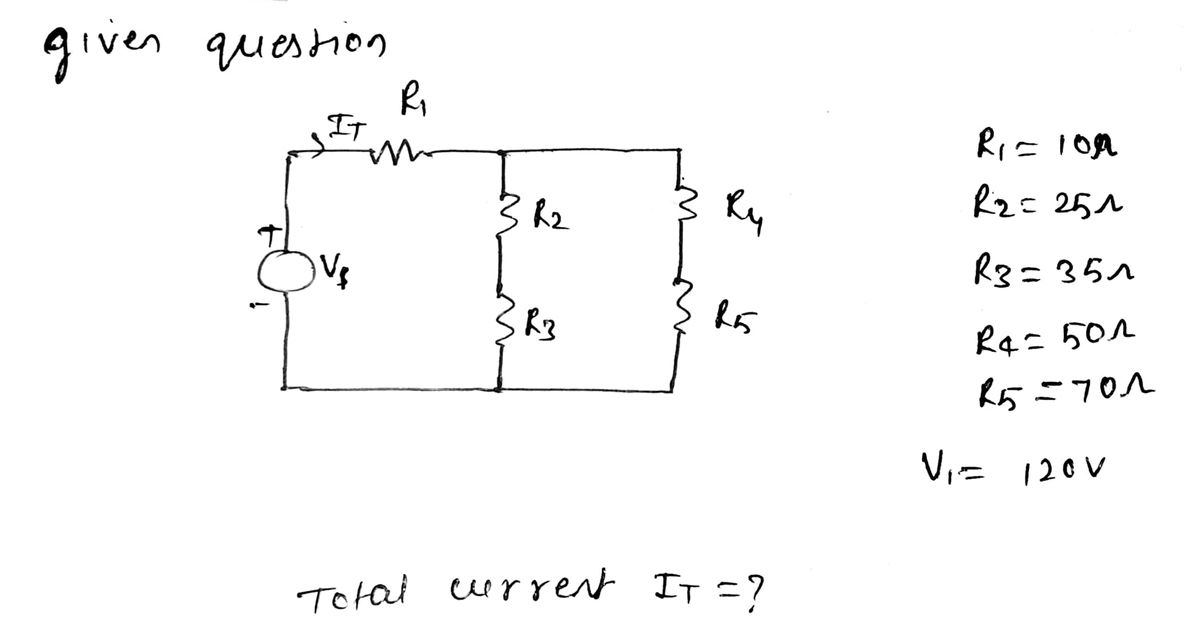
**Educational Content:** **Title: Analyzing Series and Parallel Resistor Circuits** **Problem Statement:** For a circuit with series and parallel resistors, the supply voltage, \( V_{\text{Supply}} = 120 \) Volts, and the resistors are given as follows: - \( R_1 = 10\, \Omega \) - \( R_2 = 25\, \Omega \) - \( R_3 = 35\, \Omega \) - \( R_4 = 50\, \Omega \) - \( R_5 = 70\, \Omega \) What will be the total current of the circuit? **Circuit Diagram:** The diagram depicts a circuit with the resistors distributed both in series and parallel connections. The supply voltage \( V_a \) is connected across the circuit. Here's how the resistors are connected: 1. \( R_1 \) is in series with a combination. 2. \( R_2 \) and \( R_3 \) are in parallel with each other. 3. The combination of \( R_2 \) and \( R_3 \) is in series with \( R_4 \) and these are all in parallel with \( R_5 \). **Solution Options:** - \( \quad \) ○ 3.6 Amp - \( \quad \) ○ 2.4 Amp - \( \quad \) ○ 6.4 Amp - \( \quad \) ○ 4.8 Amp **Explanation:** To solve this problem, calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit by using series and parallel formulas, then use Ohm’s Law to determine the total current flowing through the circuit. Follow these steps: 1. Calculate the parallel and series combinations. 2. Find the total equivalent resistance. 3. Apply Ohm’s Law: \( I = \frac{V}{R_{\text{total}}} \), where \( I \) is the total current. This exercise aids in understanding how to manage complex resistor networks by simplifying them into basic series and parallel parts for easy computation.
Protection System
A system that protects electrical systems from faults by isolating the problematic part from the remainder of the system, preventing power from being cut from healthy elements, improving system dependability and efficiency is the protection system. Protection devices are the equipment that are utilized to implement the protection system.
Predictive Maintenance System
Predictive maintenance technologies are designed to assist in determining the state of in-service equipment so that maintenance can be scheduled. Predictive maintenance is the application of information; proactive maintenance approaches examine the condition of equipment and anticipate when it should maintain. The purpose of predictive maintenance is to forecast when equipment will fail (depending on a variety of parameters), then prevent the failure through routine and corrective maintenance.Condition monitoring is the continual monitoring of machines during process conditions to maintain optimal machine use, which is necessary for predictive maintenance. There are three types of condition monitoring: online, periodic, and remote. Finally, remote condition monitoring allows the equipment observed from a small place and data supplied for analysis.
Preventive Maintenance System
To maintain the equipment and materials on a regular basis in order to maintain those running conditions and reduce unnecessary shutdowns due to unexpected equipment failure is called Preventive Maintenance (PM).

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images




