Explain the reactivity and orientation effects observed in each heterocycle.
a. Pyridine is less reactive than benzene in electrophilic aromatic
substitution and yields 3-substituted products.
b. Pyrrole is more reactive than benzene in electrophilic aromatic
substitution and yields 2-substituted products.

Aromatic compounds generally shows electrophilic substitution reactions. In electrophilic substitution reactions electrophile attack on benzene ring because benzene ring is electron rich due to presence of pi bonds.
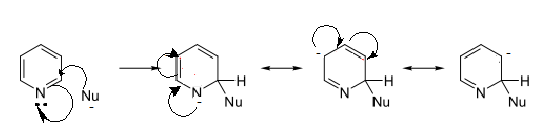
a) Pyridine is less reactive than benzene in electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction due to the presence of more electronegative atom nitrogen than carbon atom.
Nitrogen atom pull electrons towards it self and at position 3 in the pyridine the electron density is much higher as compared to position 2 and 4.Therefore, electrophile attack easily on the position 3.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









