Drive-thru Restaurant O
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
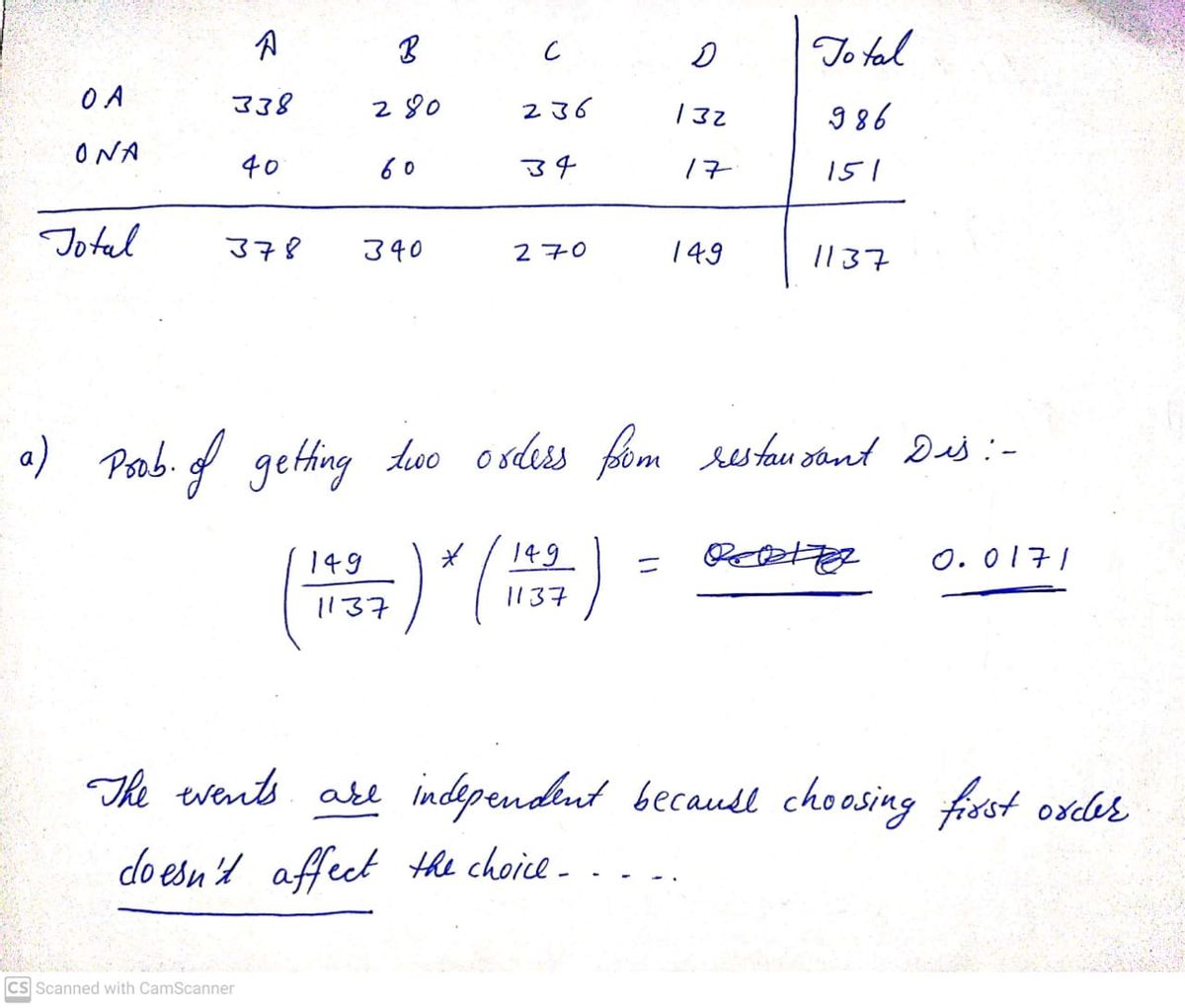
![**Data Analysis on Drive-thru Order Accuracy**
Use the data in the following table, which lists drive-thru order accuracy at popular fast food chains. Assume that orders are randomly selected from those included in the table.
| Drive-thru Restaurant | A | B | C | D |
|-----------------------|-----|-----|-----|-----|
| Order Accurate | 338 | 280 | 236 | 132 |
| Order Not Accurate | 40 | 60 | 34 | 17 |
**Problem Statement**: If two orders are selected, find the probability that they are both from Restaurant D.
**a.** Assume that the selections are made with replacement. Are the events independent?
- The probability of getting two orders from Restaurant D is \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \].
- The events \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \] independent because choosing the first order \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \] the probability of the choice of the second order.
- (Do not round until the final answer. Round to four decimal places as needed.)
**b.** Assume that the selections are made without replacement. Are the events independent?
- The probability of getting two orders from Restaurant D is \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \].
- The events \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \] independent because choosing the first order \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \] the probability of the choice of the second order.
- (Do not round until the final answer. Round to four decimal places as needed.)
**Analysis Requirements:**
- Consider whether the selections are made with or without replacement to determine if the events are independent and how they affect probability calculations.
- Fill in the blanks with appropriate probabilities and reasoning for independence based on the data provided.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F902e7e06-dd9d-47fe-961b-7a721406cdf1%2F8a6930af-be42-4e9e-9c55-47135062a5f0%2Fczuq0z_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Data Analysis on Drive-thru Order Accuracy**
Use the data in the following table, which lists drive-thru order accuracy at popular fast food chains. Assume that orders are randomly selected from those included in the table.
| Drive-thru Restaurant | A | B | C | D |
|-----------------------|-----|-----|-----|-----|
| Order Accurate | 338 | 280 | 236 | 132 |
| Order Not Accurate | 40 | 60 | 34 | 17 |
**Problem Statement**: If two orders are selected, find the probability that they are both from Restaurant D.
**a.** Assume that the selections are made with replacement. Are the events independent?
- The probability of getting two orders from Restaurant D is \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \].
- The events \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \] independent because choosing the first order \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \] the probability of the choice of the second order.
- (Do not round until the final answer. Round to four decimal places as needed.)
**b.** Assume that the selections are made without replacement. Are the events independent?
- The probability of getting two orders from Restaurant D is \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \].
- The events \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_ \] independent because choosing the first order \[ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \] the probability of the choice of the second order.
- (Do not round until the final answer. Round to four decimal places as needed.)
**Analysis Requirements:**
- Consider whether the selections are made with or without replacement to determine if the events are independent and how they affect probability calculations.
- Fill in the blanks with appropriate probabilities and reasoning for independence based on the data provided.
![**Drive-Thru Order Accuracy Analysis**
In this exercise, we analyze the drive-thru order accuracy across four popular fast food chains, labeled as Restaurants A, B, C, and D. The table below shows the number of accurate and not accurate orders for each restaurant.
| Drive-thru Restaurant | A | B | C | D |
|-----------------------|-----|-----|-----|-----|
| Order Accurate | 338 | 280 | 236 | 132 |
| Order Not Accurate | 40 | 60 | 34 | 17 |
**Objective:**
To find the probability that two orders selected are both from Restaurant D under different assumptions regarding replacement, and to determine if the events are independent.
**Analysis:**
1. **Assuming Selections with Replacement:**
- Evaluate if the selection of orders is independent.
- The formula for the probability of selecting two orders from Restaurant D with replacement is calculated as:
\[ P(D, D) = \left( \frac{\text{Number of D orders}}{\text{Total Orders}} \right)^2 \]
2. **Assuming Selections without Replacement:**
- Evaluate if the selection of orders is independent.
- The formula for the probability of selecting two orders from Restaurant D without replacement is calculated as:
\[ P(D, D) = \frac{\text{Number of D orders}}{\text{Total Orders}} \times \frac{\text{Number of D orders - 1}}{\text{Total Orders - 1}} \]
**Instructions:**
- Fill in the blanks and choose the appropriate option ("does not affect" or "affects") to evaluate independence under each scenario.
- Ensure calculations are accurate to four decimal places.
This exercise helps in understanding the concepts of probability and independence with practical application in evaluating operational performance in fast food services.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F902e7e06-dd9d-47fe-961b-7a721406cdf1%2F8a6930af-be42-4e9e-9c55-47135062a5f0%2Fmu4ali_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Drive-Thru Order Accuracy Analysis**
In this exercise, we analyze the drive-thru order accuracy across four popular fast food chains, labeled as Restaurants A, B, C, and D. The table below shows the number of accurate and not accurate orders for each restaurant.
| Drive-thru Restaurant | A | B | C | D |
|-----------------------|-----|-----|-----|-----|
| Order Accurate | 338 | 280 | 236 | 132 |
| Order Not Accurate | 40 | 60 | 34 | 17 |
**Objective:**
To find the probability that two orders selected are both from Restaurant D under different assumptions regarding replacement, and to determine if the events are independent.
**Analysis:**
1. **Assuming Selections with Replacement:**
- Evaluate if the selection of orders is independent.
- The formula for the probability of selecting two orders from Restaurant D with replacement is calculated as:
\[ P(D, D) = \left( \frac{\text{Number of D orders}}{\text{Total Orders}} \right)^2 \]
2. **Assuming Selections without Replacement:**
- Evaluate if the selection of orders is independent.
- The formula for the probability of selecting two orders from Restaurant D without replacement is calculated as:
\[ P(D, D) = \frac{\text{Number of D orders}}{\text{Total Orders}} \times \frac{\text{Number of D orders - 1}}{\text{Total Orders - 1}} \]
**Instructions:**
- Fill in the blanks and choose the appropriate option ("does not affect" or "affects") to evaluate independence under each scenario.
- Ensure calculations are accurate to four decimal places.
This exercise helps in understanding the concepts of probability and independence with practical application in evaluating operational performance in fast food services.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman