Draw an “energy level diagram” for a calcium (Ca) atom. HINT: Use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons that are present in a krypton atom. An empty (no electrons) energy level diagram for multi-electron atoms is shown on the left. Electrons are arranged (configured) into the orbitals in the way that results in the lowest possible energy. Nature does this by obeying the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rules. See the hint from the previous question (3.2) for more details. EXPLANATION: A calcium atom has 20 protons and therefore 20 electrons. Electrons are arranged (configured) into the orbitals in the way that results in the lowest possible energy. Nature does this by obeying the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rules. See the hint from the previous question (3.2) for more details. Note that the 4s orbital fills before the 3d orbital because the 4s orbital lower in energy than the 3d orbitals (the 3d orbitals are not shown here because they do not contain electrons).
Electron Affinity
When an element undergoes a chemical reaction, it either gains energy or loses energy. This gain or loss of energy is due to the phenomena that occur at atomic level. During reaction, atoms either gain electrons from other atoms or lose electrons to other atoms, and in that process, energy is produced.
P-Block Elements
Elements which are present on the right side of the periodic table are called p-block elements. In addition to the noble gases, they include the families of boron, mercury, nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine. These elements have diverse real-life implementations that we regularly experience around us.
Metals and Non-metals
The periodic table is composed of metals, semi-metals and nonmetal elements. The physical and chemical properties of metals and nonmetals differ from each other. The study of metals and nonmetals will help one to understand the appropriate application of the particular element.
Draw an “energy level diagram” for a calcium (Ca) atom.
HINT: Use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons that are present in a krypton atom. An empty (no electrons) energy level diagram for multi-electron atoms is shown on the left. Electrons are arranged (configured) into the orbitals in the way that results in the lowest possible energy. Nature does this by obeying the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rules. See the hint from the previous question (3.2) for more details. EXPLANATION: A calcium atom has 20 protons and therefore 20 electrons. Electrons are arranged (configured) into the orbitals in the way that results in the lowest possible energy. Nature does this by obeying the Aufbau Principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s Rules. See the hint from the previous question (3.2) for more details. Note that the 4s orbital fills before the 3d orbital because the 4s orbital lower in energy than the 3d orbitals (the 3d orbitals are not shown here because they do not contain electrons).
Can you help me, please?
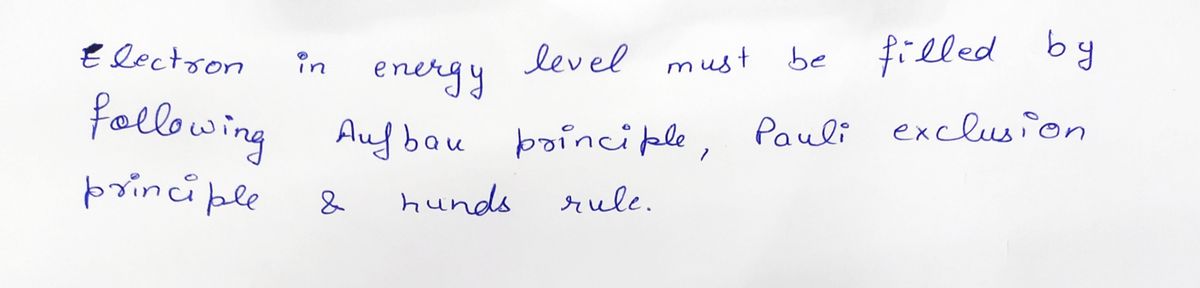
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









