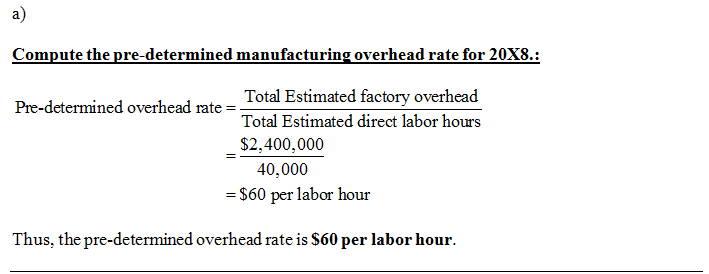
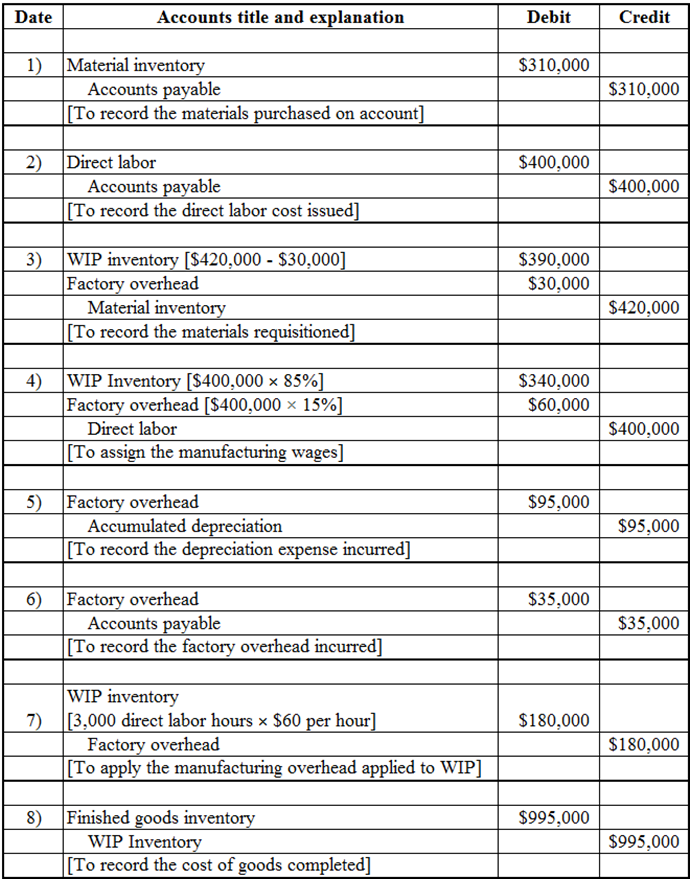
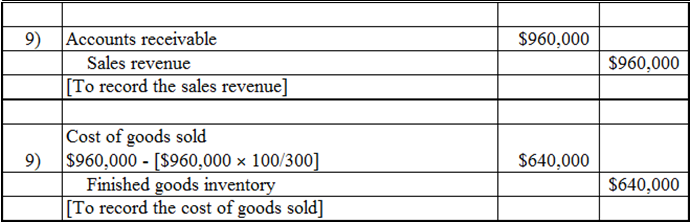
Discussion Cutters does customized, hand-crafted memorabilia, in which each batch of items is a job. The company has a highly labour intensive production process, so it allocates manufacturing overhead based on direct labour hours. Starz pre-determined overhead application rate for 20X8 was computed from the following data: Total estimated factory overheads $2,400,000 Total estimated direct labour hours 40,000 At the end of May 20X8, Cutters reported the following inventories: Materials Inventory WIP Inventory Finished Goods Inventory Bal. $208,000 Bal. $176,000 Bal. $95,000 During June 20X8, Cutters actually used 3,000 direct labour hours and recorded the following transactions. (1) Purchased materials on account $310,000 (ii) Manufacturing wages incurred $400,000 (i) Materials requisitioned (includes $30,000 of indirect materials) $420,000 (iv) Assigned manufacturing wages, 85% direct labour, 15% indirect labour (v) Depreciation expense on factory equipment used on the different jobs $95,000 (v) Other manufacturing overhead incurred $35,000 (vi) Allocated manufacturing overhead for June 20x8 (vii) Cost of jobs completed (vii) Cost of jobs sold (on account) at a margin of 33%% on sales $995,000 $960,000 (a) Compute Cutters predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for 20X8. (b) State the journal entries necessary to record the above transactions in the general journal. Assume that Cutters uses the perpetual inventory system. (c) Post the manufacturing overhead transactions to the Manufacturing Overhead T-account and state the balance on the account before performing end of period closing entries. Show the journal entries necessary to dispose of the variance. (d) What is the balance in the Cost of Goods Sold account after the adjustment? (e) Compute Cutters gross profit earned on the jobs completed. (f Open T-accounts for Materials Inventory, Work in Process Inventory and Finished Goods Inventory. Post the appropriate entries to these accounts & determine the ending account balances.
Process Costing
Process costing is a sort of operation costing which is employed to determine the value of a product at each process or stage of producing process, applicable where goods produced from a series of continuous operations or procedure.
Job Costing
Job costing is adhesive costs of each and every job involved in the production processes. It is an accounting measure. It is a method which determines the cost of specific jobs, which are performed according to the consumer’s specifications. Job costing is possible only in businesses where the production is done as per the customer’s requirement. For example, some customers order to manufacture furniture as per their needs.
ABC Costing
Cost Accounting is a form of managerial accounting that helps the company in assessing the total variable cost so as to compute the cost of production. Cost accounting is generally used by the management so as to ensure better decision-making. In comparison to financial accounting, cost accounting has to follow a set standard ad can be used flexibly by the management as per their needs. The types of Cost Accounting include – Lean Accounting, Standard Costing, Marginal Costing and Activity Based Costing.

Job costing: It is a method of costing where in all the costs like direct material, direct labor and manufacturing overhead are accumulated to a particular job. This method is suitable for jobs where the work is to be performed according to the specifications of a customer and in separate batches.
Pre-determined overhead allocate rate: It the rate of allocating the expected overheads to the actual units or hours for a specific accounting period.
Raw materials: It is the basic input required to manufacture the finished products. The raw materials are processed by incurring conversion costs and other overhead to convert them into finished products.
Manufacturing overhead: It is the indirect cost incurred as a part of manufacturing the products. These costs are not directly related to the units manufactured. So they are allocated to the manufactured units based on estimated cost drivers.
Work-in process: This is the cost of units which were semi-finished in a particular period. Further work should be done and cost should be incurred to make them into finished products.
Finished goods: These are the units which were completed by the manufacturing process and were ready to sale.
Under/over applied overhead: If the overhead applied is more than the actual overhead, then the overhead is said to be over applied. If the overhead applied is less than the actual overhead then the overhead is said to be under applied.
In case of multiple sub-parts in a question, only first, 3 sub parts will be answered. If you want other sub-parts to be answered, Please post the entire question once again and mention the sub-parts to be answered.
b)
Prepare the journal entries:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images









